开发环境:
主机:Ubuntu 20.04
开发板:MYD-YF135开发板
Video for Linuxtwo(Video4Linux2)简称V4L2,是V4L的改进版。V4L2是linux操作系统下用于采集图片、视频和音频数据的API接口,配合适当的视频采集设备和相应的驱动程序,可以实现图片、视频、音频等的采集。在远程会议、可视电话、视频监控系统和嵌入式多媒体终端中都有广泛的应用。本文将基于V4L2使用usb摄像头(UVC)拍照。
1 查看内核对USB摄像头
当插入UVC摄像头就会以下打印信息。
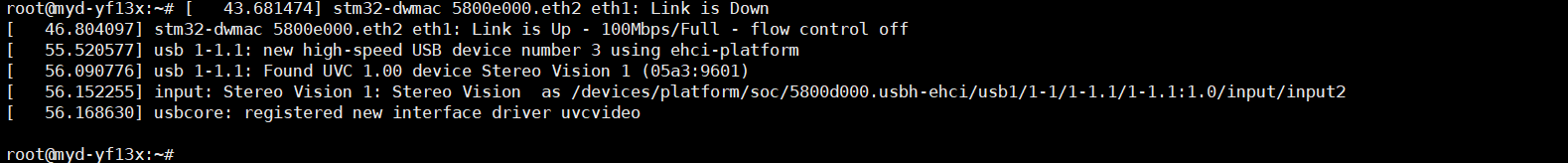
在dev目录下也会有相应的设备。

如果插入多个摄像头,设备名后缀数字依次增加,如: video1 video2 video3。
摄像头识别检测和格式支持查询
# v4l2-ctl --list-devices

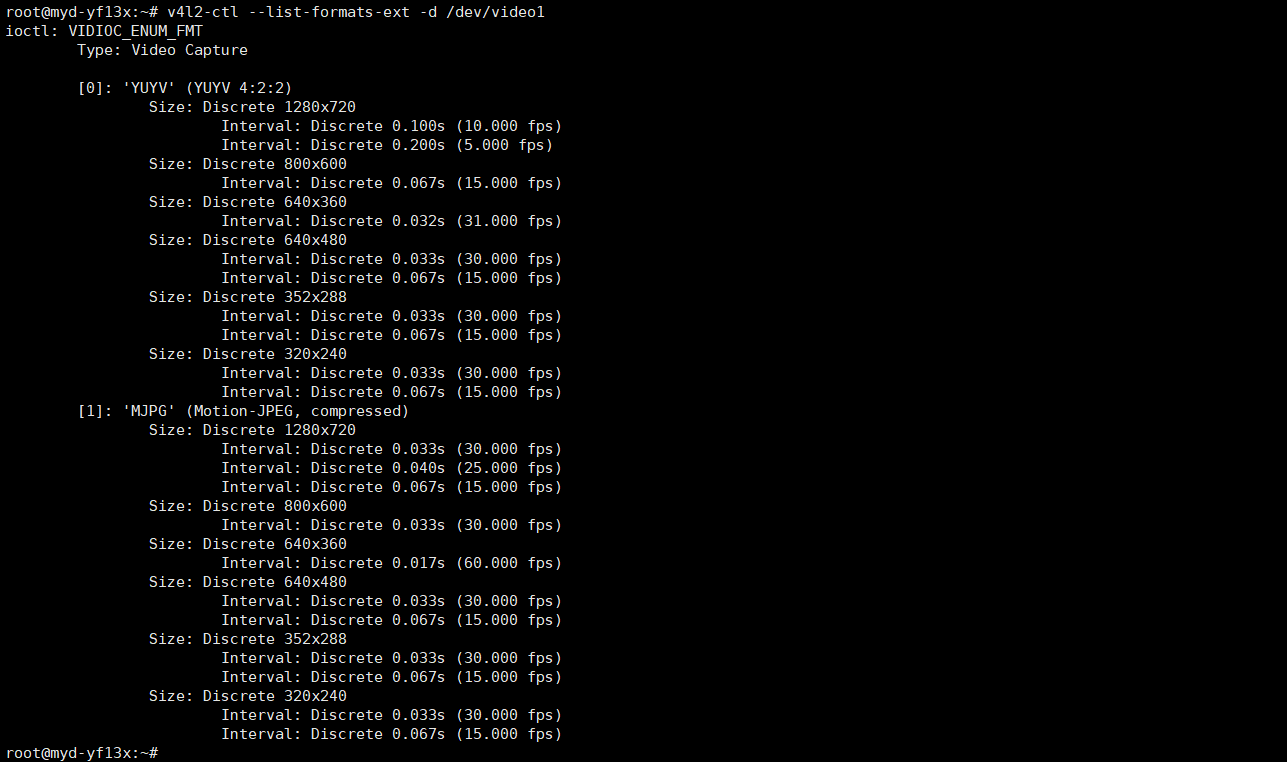
格式支持查询:
# v4l2-ctl --list-formats-ext -d /dev/video1
2 V4L2拍照应用实现
2.1 V4L2拍照原理与实现
在Linux下,所有外设都被看成一种特殊的文件,也就是一切皆文件,Linux中所有的外设均可像访问普通文件一样对其进行读写操作。
V4L2在include/linux/videodev.h文件中定义了一些重要的数据结构,在采集图像的过程中,就是通过对这些数据的操作来获得最终的图像数据。Linux系统V4L2的能力可在Linux内核编译阶段配置,默认情况下都有此开发接口。
在Linux中V4L2拍照的调用过程如下图所示。
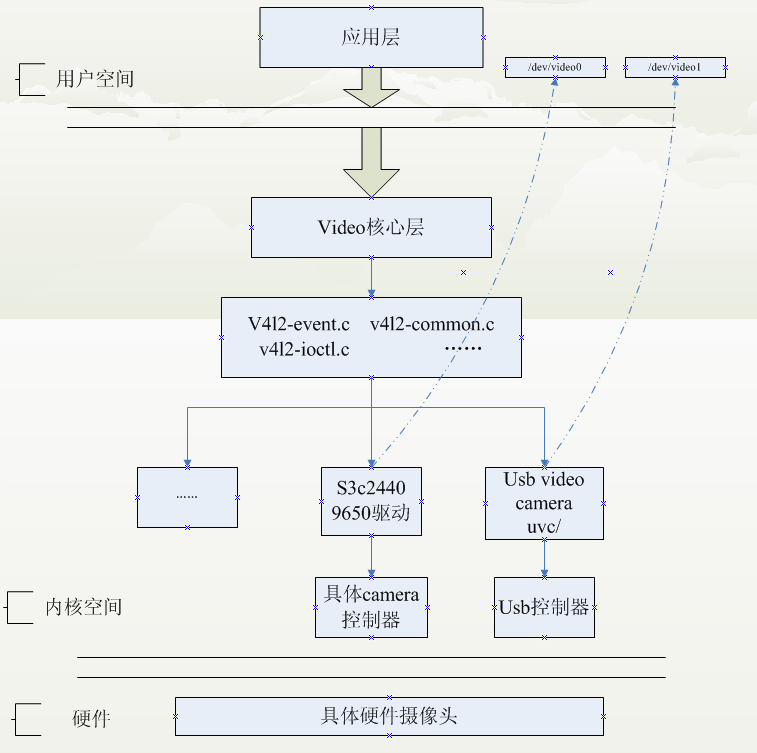
V4L2支持两种方式来采集图像:内存映射方式(mmap)和直接读取方式(read)。前者一般用于连续视频数据的采集,后者常用于静态图片数据的采集。
主要分为五个步骤:
首先,打开设备文件,参数初始化,通过V4L2接口设置图像的采集窗口、采集的点阵大小和格式。
其次,申请若干图像采集的帧缓冲区,便于应用程序读取/处理视频数据。
第三,将申请到的帧缓冲区在数据采集输入队列排队,并启动图片采集。
第四,驱动开始图像数据的采集,应用程序从数据采集输出队列取出帧缓冲区,处理完后,将帧缓冲区重新放入数据采集输入队列,循环往复采集连续的数据;
第五,停止数据采集。
完整代码如下:
【usb_camera.c】
#include "usb_camera.h"
#define DEBUG
buffer *user_buf = NULL;
static unsigned int n_buffer = 0;
static unsigned long file_length;
buffer *user_buf = NULL;
static unsigned int n_buffer = 0;
static unsigned long file_length;
char picture_name[64] ="stm32mp_picture";
int num = 0;
int open_camer_device(char * videoDev)
{
int fd;
if((fd = open(videoDev,O_RDWR | O_NONBLOCK)) < 0)
{
perror("Fail to open");
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
return fd;
}
int init_camer_device(int fd)
{
struct v4l2_fmtdesc fmt;
struct v4l2_capability cap;
struct v4l2_format stream_fmt;
int ret;
ret = ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_QUERYCAP,&cap);
if(ret < 0)
{
perror("FAIL to ioctl VIDIOC_QUERYCAP");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE))
{
perror("The Current device is not a video capture device\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(!(cap.capabilities & V4L2_CAP_STREAMING))
{
perror("The Current device does not support streaming i/o\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
memset(&fmt,0,sizeof(fmt));
fmt.index = 0;
fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
while((ret = ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_ENUM_FMT,&fmt)) == 0)
{
fmt.index ++ ;
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("{pixelformat = %c%c%c%c},description = '%s'\n",
fmt.pixelformat & 0xff,(fmt.pixelformat >> 8)&0xff,
(fmt.pixelformat >> 16) & 0xff,(fmt.pixelformat >> 24)&0xff,
fmt.description);
#endif
}
stream_fmt.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
stream_fmt.fmt.pix.width = 680;
stream_fmt.fmt.pix.height = 480;
stream_fmt.fmt.pix.pixelformat = V4L2_PIX_FMT_MJPEG;
stream_fmt.fmt.pix.field = V4L2_FIELD_INTERLACED;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_S_FMT,&stream_fmt))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
file_length = stream_fmt.fmt.pix.bytesperline * stream_fmt.fmt.pix.height;
init_mmap(fd);
return 0;
}
int init_mmap(int fd)
{
int i = 0;
struct v4l2_requestbuffers reqbuf;
bzero(&reqbuf,sizeof(reqbuf));
reqbuf.count = 4;
reqbuf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
reqbuf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_REQBUFS,&reqbuf))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl 'VIDIOC_REQBUFS'");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
n_buffer = reqbuf.count;
#ifdef DEBUG
printf("n_buffer = %d\n",n_buffer);
#endif
user_buf = calloc(reqbuf.count,sizeof(*user_buf));
if(user_buf == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Out of memory\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
for(i = 0; i < n_buffer; i ++)
{
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
bzero(&buf,sizeof(buf));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = i;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_QUERYBUF,&buf))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl : VIDIOC_QUERYBUF");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
user_buf[i].length = buf.length;
user_buf[i].start =
mmap(
NULL,
buf.length,
PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE,
MAP_SHARED,
fd,buf.m.offset
);
if(MAP_FAILED == user_buf[i].start)
{
perror("Fail to mmap");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
return 0;
}
int start_capturing(int fd)
{
unsigned int i;
enum v4l2_buf_type type;
for(i = 0;i < n_buffer;i ++)
{
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
bzero(&buf,sizeof(buf));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
buf.index = i;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_QBUF,&buf))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl 'VIDIOC_QBUF'");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_STREAMON,&type))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl 'VIDIOC_STREAMON'");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return 0;
}
int mainloop(int fd)
{
int count = 2;
while(count-- > 0)
{
for(;;)
{
fd_set fds;
struct timeval tv;
int r;
FD_ZERO(&fds);
FD_SET(fd,&fds);
tv.tv_sec = 2;
tv.tv_usec = 0;
r = select(fd + 1,&fds,NULL,NULL,&tv);
if(-1 == r)
{
if(EINTR == errno)
continue;
perror("Fail to select");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(0 == r)
{
fprintf(stderr,"select Timeout\n");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if(read_frame(fd))
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
int process_image(void *addr,int length)
{
FILE *fp;
char name[20];
sprintf(name,"%s%d.jpg",picture_name,num ++);
if((fp = fopen(name,"w")) == NULL)
{
perror("Fail to fopen");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
fwrite(addr,length,1,fp);
usleep(500);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
int read_frame(int fd)
{
struct v4l2_buffer buf;
unsigned int i;
bzero(&buf,sizeof(buf));
buf.type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
buf.memory = V4L2_MEMORY_MMAP;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_DQBUF,&buf))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl 'VIDIOC_DQBUF'");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
assert(buf.index < n_buffer);
{
#ifdef DEBUG
printf ("buf.index dq is %d,\n",buf.index);
#endif
}
process_image(user_buf[buf.index].start,user_buf[buf.index].length);
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_QBUF,&buf))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl 'VIDIOC_QBUF'");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return 1;
}
void stop_capturing(int fd)
{
enum v4l2_buf_type type;
type = V4L2_BUF_TYPE_VIDEO_CAPTURE;
if(-1 == ioctl(fd,VIDIOC_STREAMOFF,&type))
{
perror("Fail to ioctl 'VIDIOC_STREAMOFF'");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return;
}
void uninit_camer_device()
{
unsigned int i;
for(i = 0;i < n_buffer;i ++)
{
if(-1 == munmap(user_buf[i].start,user_buf[i].length))
{
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
}
free(user_buf);
return;
}
void close_camer_device(int fd)
{
if(-1 == close(fd))
{
perror("Fail to close fd");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
return;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int camera_fd;
if(argc == 2 )
{
camera_fd = open_camer_device(argv[1]);
init_camer_device(camera_fd);
start_capturing(camera_fd);
num = 0;
mainloop(camera_fd);
stop_capturing(camera_fd);
uninit_camer_device(camera_fd);
close_camer_device(camera_fd);
printf("Camera get pic success!\n");
}
else
{
printf("Please input video device!\n");
}
return 0;
}
【usb_camera.h】
#ifndef _USB_CAMERA_H_
#define _USB_CAMERA_H_
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <getopt.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <asm/types.h>
#include <linux/videodev2.h>
#define VIDEO_DEV "/dev/video9"
typedef struct _buffer
{
void *start;
size_t length;
}buffer;
int open_camer_device(char * videoDev);
int init_mmap(int fd);
int init_camer_device(int fd);
int start_capturing(int fd);
int process_image(void *addr,int length);
int read_frame(int fd);
int mainloop(int fd);
void stop_capturing(int fd);
void uninit_camer_device();
void close_camer_device(int fd);
void camera_get_image(void);
#endif
【Makefile】
ARCH=arm32
CROSS=${CC}
all: usb_camera
sudo scp usb_camera root@192.168.19.130:/home/root
usb_camera:usb_camera.c
$(CROSS) -o usb_camera usb_camera.c
clean:
@rm -vf usb_camera *.o *~
值得注意的是,Makefile中通过scp将编译好的程序拷贝到开发板,需要根据修改相应开发板的IP地址。当然也可通过其他方式拷贝程序。
2.2 编译测试
接下来就是编译下载测试了。
1.编译
# make

值得注意的是,上面的IP地址是开发板的IP,密码是开发板的登陆密码。
2.测试
接下来在MYD-YF135开发板中运行拍照程序。

笔者一次拍两张,当然也可以连续拍很多,在代码中可以修改。最后将照片传到主机查看。照片大小在代码中可以调整,可以通过参数传进去。
 电子发烧友论坛
电子发烧友论坛 /9
/9 









 淘帖
淘帖 6614
6614


