前言
ACM32F403支持CORTEX-M4的DSP指令,ARM的CMSIS提供了相应的DSP库包括算数运算,滤波,变换等,现在简单的体验下算数运算。
过程
测试方式是对DSP算法库和开发环境提供的math库进行对比。
分别进行32组 sin(x)^2+ cos(x)^2的计算,如果值与1的偏差小于(0.0001f)认为计算正确。
重复100000次,分别计算两种计算方法的时间。
在\DSP\demo_arm_sin_cos的基础上进行修改。
App.c代码如下添加一组测试APP_math_Sin_Cos_Test
代码如下
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
* Copyright (C) 2010-2012 ARM Limited. All rights reserved.
*
* $Date: 12. March 2014
* $Revision: V1.4.3
*
* Project: CMSIS DSP Library
* Title:
*
* Description: Example code demonstrating sin and cos calculation of input signal.
*
* Target Processor: Cortex-M4/Cortex-M3/Cortex-M33
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
* - Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* - Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in
* the documentation and/or other materials provided with the
* distribution.
* - Neither the name of ARM LIMITED nor the names of its contributors
* may be used to endorse or promote products derived from this
* software without specific prior written permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS
* FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
* COPYRIGHT OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT,
* INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING,
* BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES;
* LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
* CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
* LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN
* ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE
* POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
* -------------------------------------------------------------------- */
/**
* @ingroup groupExamples
*/
/**
* @defgroup SinCosExample SineCosine Example
*
* \par Description:
* \par
* Demonstrates the Pythagorean trignometric identity with the use of Cosine, Sine, Vector
* Multiplication, and Vector Addition functions.
*
* \par Algorithm:
* \par
* Mathematically, the Pythagorean trignometric identity is defined by the following equation:
* <pre>sin(x) * sin(x) + cos(x) * cos(x) = 1</pre>
* where \c x is the angle in radians.
*
* \par Block Diagram:
* \par
* \image html sinCos.gif
*
* \par Variables Description:
* \par
* \li \c testInput_f32 array of input angle in radians
* \li \c testOutput stores sum of the squares of sine and cosine values of input angle
*
* \par CMSIS DSP Software Library Functions Used:
* \par
* - arm_cos_f32()
* - arm_sin_f32()
* - arm_mult_f32()
* - arm_add_f32()
*
* <b> Refer </b>
*
******************************************************************************
*/
#include "APP.h"
#include "arm_math.h"
#include <math.h>
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
* Defines each of the tests performed
* ------------------------------------------------------------------- */
#define MAX_BLOCKSIZE 32
#define DELTA (0.0001f)
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
* Test input data for Floating point sin_cos example for 32-blockSize
* Generated by the MATLAB randn() function
* ------------------------------------------------------------------- */
const float32_t testInput_f32[MAX_BLOCKSIZE] =
{
-1.244916875853235400, -4.793533929171324800, 0.360705030233248850, 0.827929644170887320, -3.299532218312426900, 3.427441903227623800, 3.422401784294607700, -0.108308165334010680,
0.941943896490312180, 0.502609575000365850, -0.537345278736373500, 2.088817392965764500, -1.693168684143455700, 6.283185307179590700, -0.392545884746175080, 0.327893095115825040,
3.070147440456292300, 0.170611405884662230, -0.275275082396073010, -2.395492805446796300, 0.847311163536506600, -3.845517018083148800, 2.055818378415868300, 4.672594161978930800,
-1.990923030266425800, 2.469305197656249500, 3.609002606064021000, -4.586736582331667500, -4.147080139136136300, 1.643756718868359500, -1.150866392366494800, 1.985805026477433800
};
const float32_t testRefOutput_f32 = 1.000000000;
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
* Declare Global variables
* ------------------------------------------------------------------- */
uint32_t blockSize = 32;
float32_t testOutput;
float32_t cosOutput;
float32_t sinOutput;
float32_t cosSquareOutput;
float32_t sinSquareOutput;
/* ----------------------------------------------------------------------
* Max magnitude FFT Bin test
* ------------------------------------------------------------------- */
arm_status status;
extern uint32_t gu32_SystemCount;
void APP_ARM_Sin_Cos_Test(void)
{
float32_t diff;
uint32_t i;
uint32_t t0 = gu32_SystemCount;
uint32_t t1=0;
for(int j=0; j<100000;j++)
{
for(i=0; i< blockSize; i++)
{
cosOutput = arm_cos_f32(testInput_f32[i]);
sinOutput = arm_sin_f32(testInput_f32[i]);
arm_mult_f32(&cosOutput, &cosOutput, &cosSquareOutput, 1);
arm_mult_f32(&sinOutput, &sinOutput, &sinSquareOutput, 1);
arm_add_f32(&cosSquareOutput, &sinSquareOutput, &testOutput, 1);
/* absolute value of difference between ref and test */
diff = fabsf(testRefOutput_f32 - testOutput);
/* Comparison of sin_cos value with reference */
if (diff > DELTA)
{
status = ARM_MATH_TEST_FAILURE;
printfS("ARM Sin_Cos Test Fail!!!\r\n");
}
if ( status == ARM_MATH_TEST_FAILURE)
{
while (1);
}
}
}
t1 = gu32_SystemCount;
printfS("ARM Sin_Cos Test Success %d ms!!!\r\n",t1-t0);
///while (1);
}
void APP_math_Sin_Cos_Test(void)
{
float32_t diff;
uint32_t i;
uint32_t t0 = gu32_SystemCount;
uint32_t t1=0;
for(int j=0;j<100000;j++)
{
for(i=0; i< blockSize; i++)
{
cosOutput = cosf(testInput_f32[i]);
sinOutput = sinf(testInput_f32[i]);
cosSquareOutput = cosOutput*cosOutput;
sinSquareOutput = sinOutput*sinOutput;
testOutput = cosSquareOutput + sinSquareOutput;
/* absolute value of difference between ref and test */
diff = fabsf(testRefOutput_f32 - testOutput);
/* Comparison of sin_cos value with reference */
if (diff > DELTA)
{
status = ARM_MATH_TEST_FAILURE;
printfS("math Sin_Cos Test Fail!!!\r\n");
}
if ( status == ARM_MATH_TEST_FAILURE)
{
while (1);
}
}
}
t1 = gu32_SystemCount;
printfS("math Sin_Cos Test Success %d mS!!!\r\n",t1-t0);
while (1);
}
测试结果如下
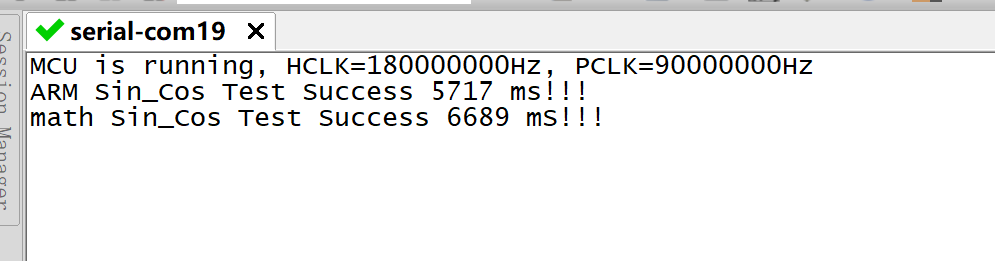
可以看到使用DSP库运行时间是math库的85%时间左右
工程中DSP库是以lib提供,源码可以参考CMSIS的git仓库。对比math来说提升不是特别大,因为c的math库实际也是会按照硬件DSP指令进行编译,除非编译器指定了不使用硬件浮点编译。所以区别不大,如果对比软件实现肯定提升就很大了,这里就不测试使用纯软件实现测试了。
总结
ARM的DSP库是专门针对CORTEX-M4等支持DSP指令的芯片提供的,包括算数运算,滤波,各种变换等,可以充分发挥CORTEX-M4的DSP优势,且使用方便。但是针对BLDC控制算法等需要频繁调用三角运算的场景来说,这还不够,所以本芯片有一个特色功能就是硬件算数加速,这个下次再测试。
 /9
/9 