
六岳微 LY-F335 开发板采用 32 位自主内核设计,主频 150MHz,集成了大量外设部件,具有高性能、低功耗和高可靠性的特点。应用于电机控制、光伏逆变、数字电源等领域。
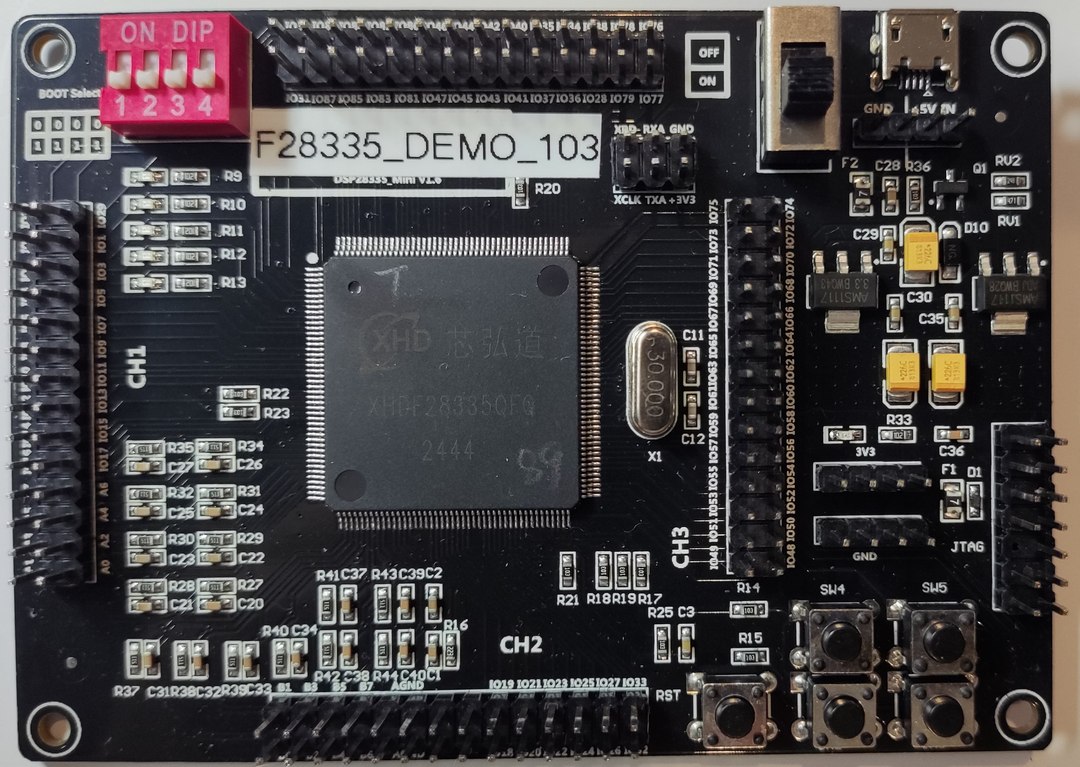
动态展示见顶部视频。
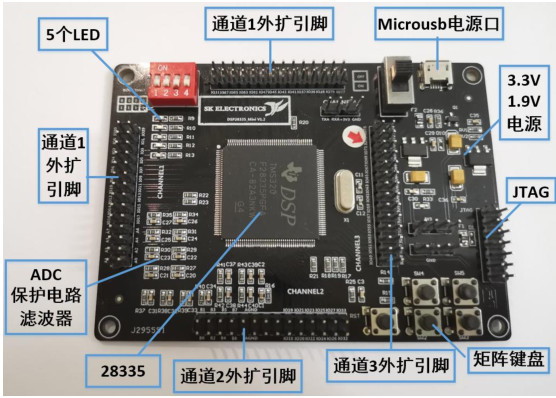
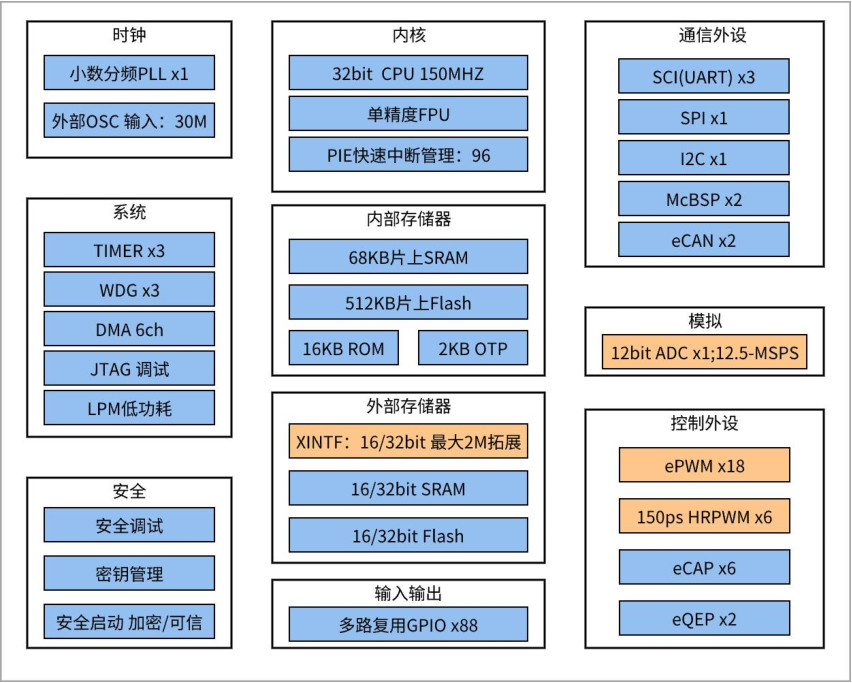
XHDF28335 是一款全自主正向设计的高性能浮点DSP芯片,采用32位自主内核设计,主频为150MHz,内部集成了丰富的外设资源,支持多种通信协议,具有 高性能、低功耗和高可靠性的特点。
广泛应用于变频器、电机控制、光伏逆变、数字电源等领域。

详见:芯弘道 | XHDF28335 .
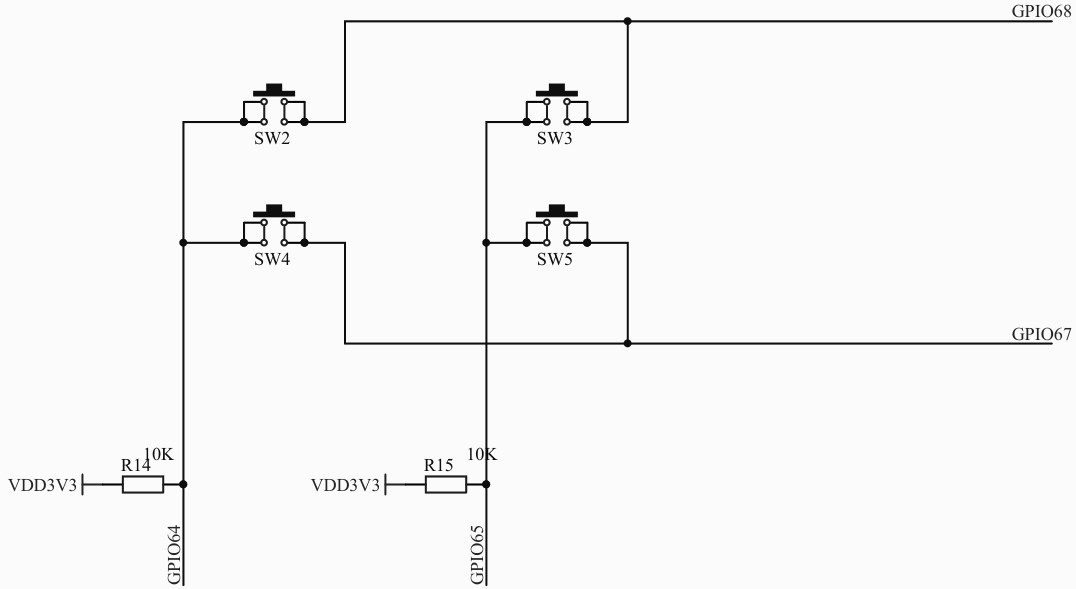
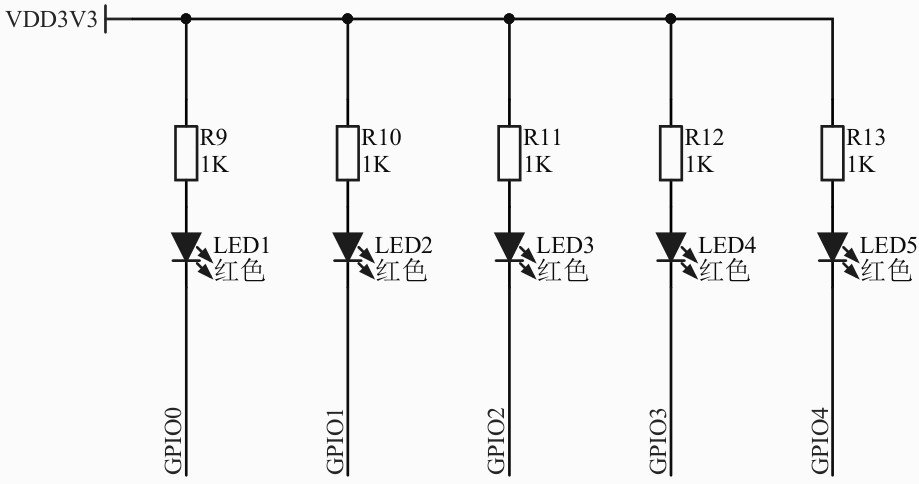
包括 MCU、供电、GPIO、外设、ADC等。
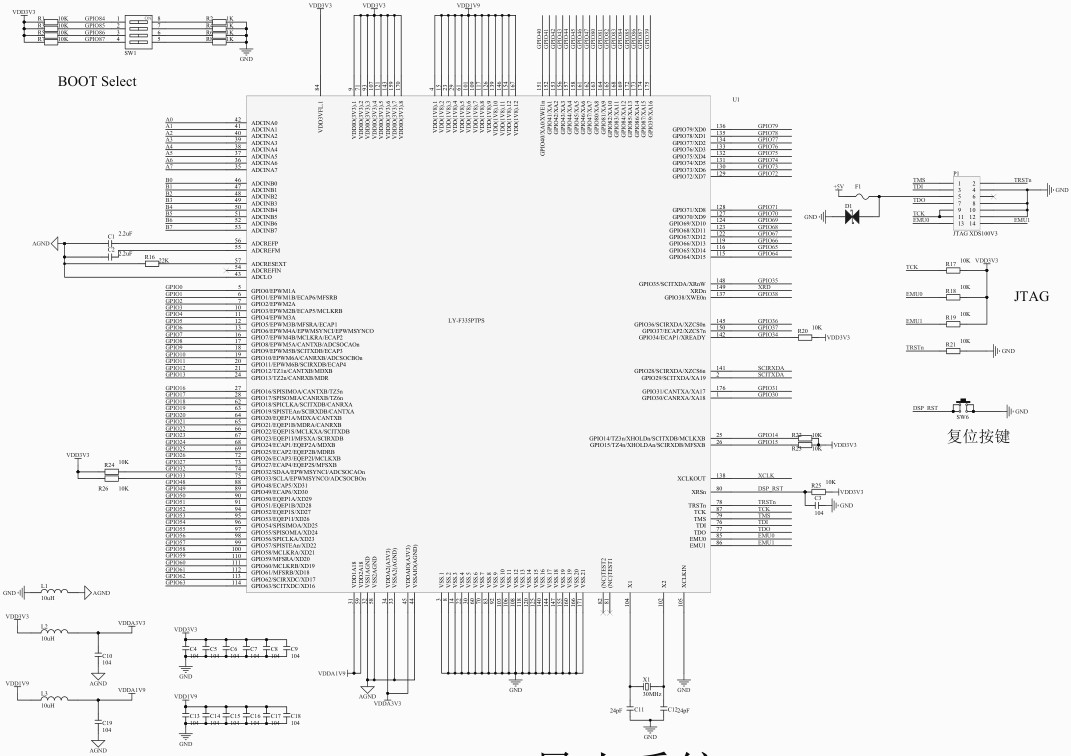
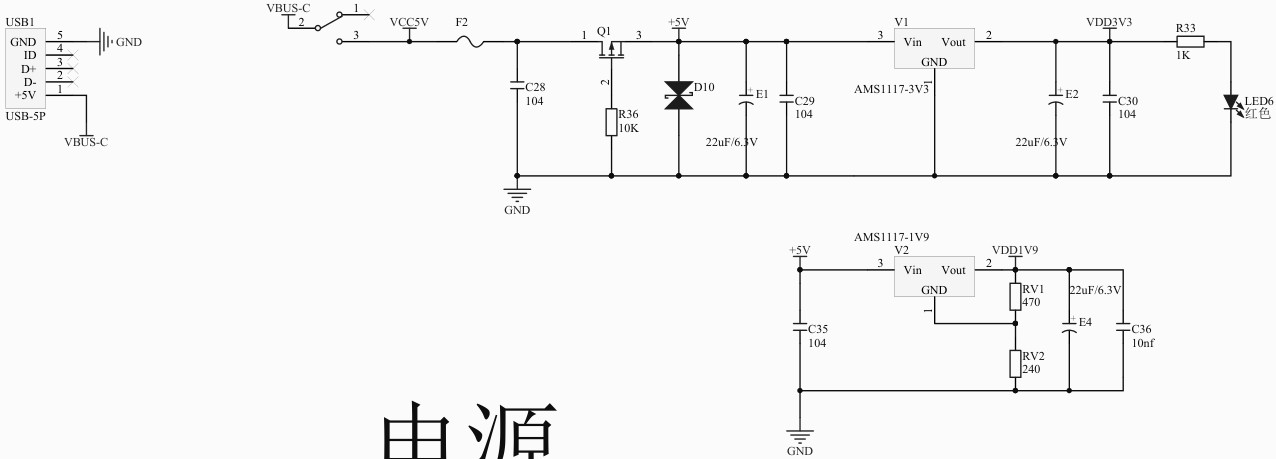
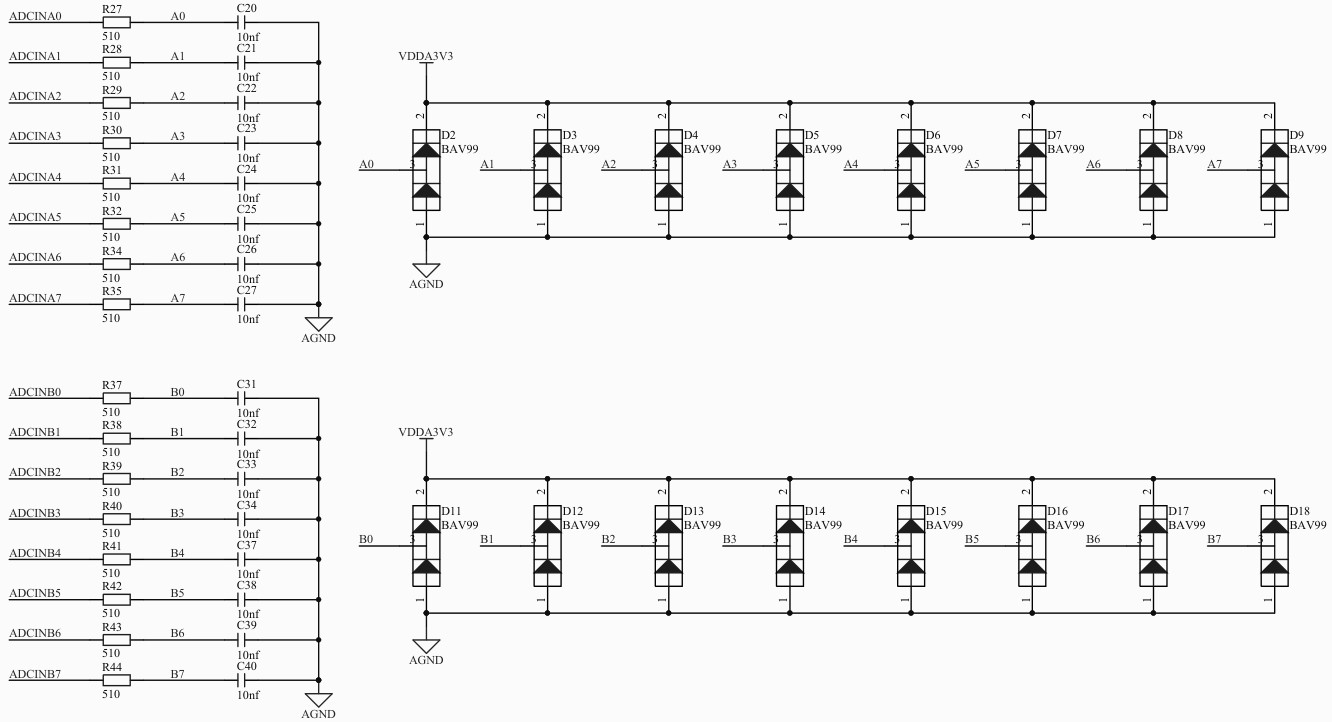
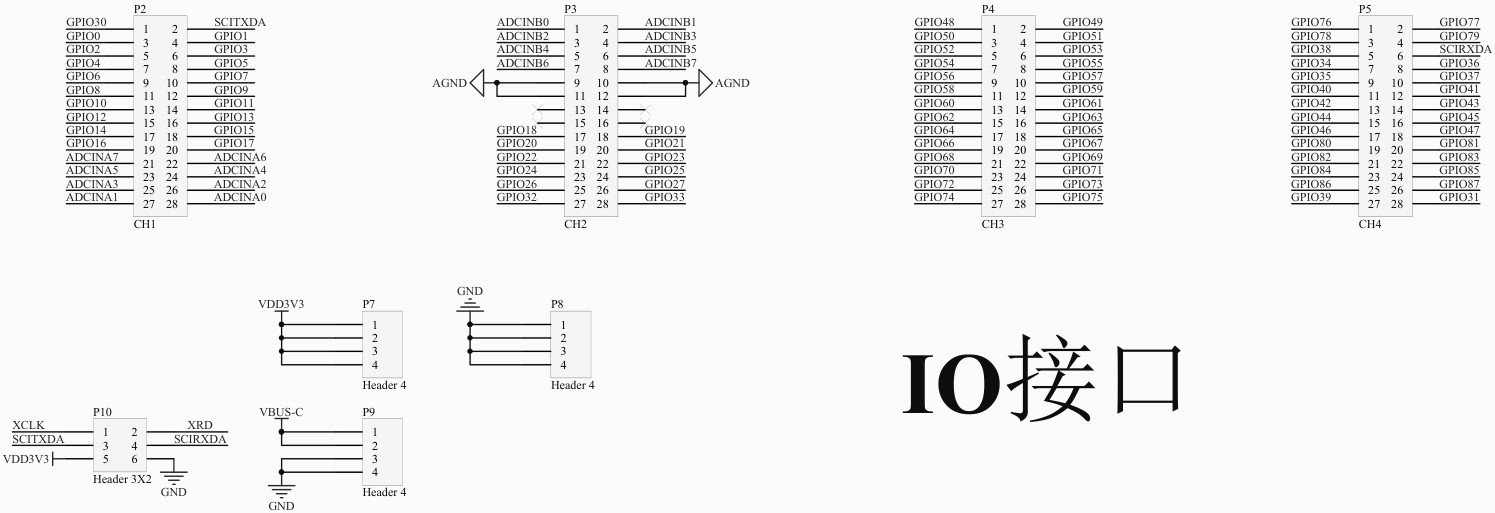
进入产品资料链接目录 LY-F335/软件开发资源 ,下载 SDK 压缩包;
下载 C2000Ware_3_04_00_00_setup.exe 并安装 C2000Ware 软件;
下载 ti_cgt_c2000_6.4.2_windows_installer.exe 并安装 C2000 Code Generation Tools;
下载并安装 CCSTUDIO IDE .
详细安装步骤见压缩包内教程。
File - Import Project ,选择 C2000 安装例程 F:\ti\c2000\C2000Ware_3_04_00_00\device_support\f2833x\examples\gpio_toggle 文件夹;
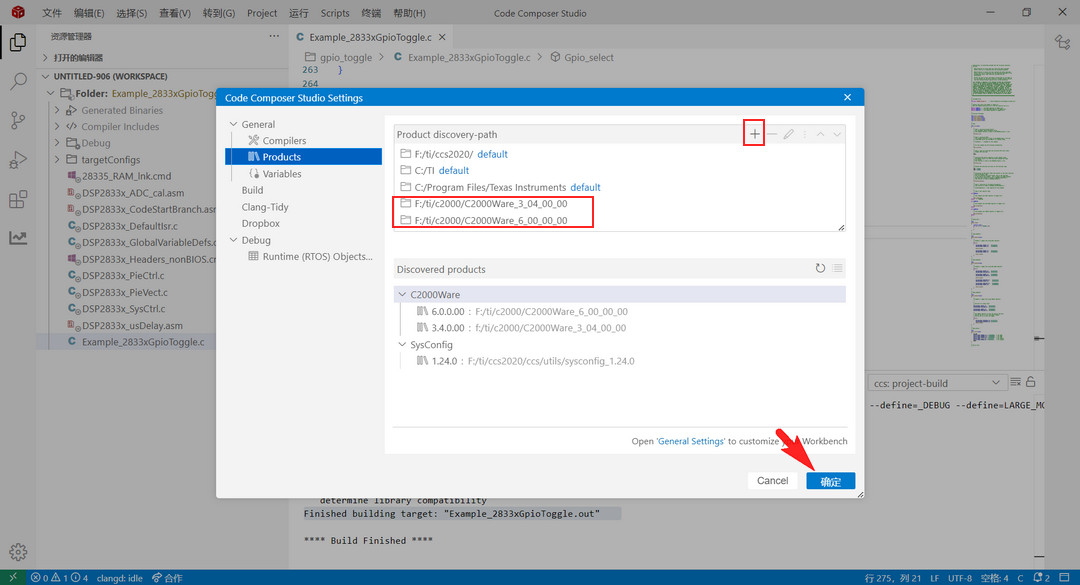
File - 首选项 - Code Composer Studio Settings - General - Products,添加 C2000Ware 安装文件夹路径;
右键工程 - Build Project
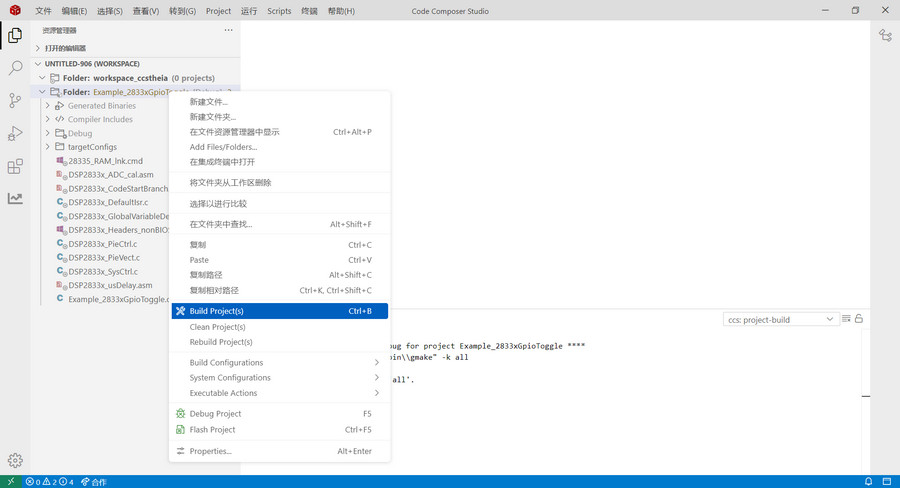
终端打印 构建完成,生成 *.out 文件
Finished building target: "Example_2833xGpioToggle.out"
双击打开左侧 Demo 目录文件 Example_2833xGpioToggle.c
#include "DSP28x_Project.h" // Device Headerfile and Examples Include File
//
// Defines that select the example to compile in.
// Only one example should be set as 1 the rest should be set as 0.
//
#define EXAMPLE1 1 // Use DATA registers to toggle I/O's
#define EXAMPLE2 0 // Use SET/CLEAR registers to toggle I/O's
#define EXAMPLE3 0 // Use TOGGLE registers to toggle I/O's
//
// Function Prototypes
//
void delay_loop(void);
void Gpio_select(void);
void Gpio_example1(void);
void Gpio_example2(void);
void Gpio_example3(void);
//
// Main
//
void main(void)
{
//
// Step 1. Initialize System Control:
// PLL, WatchDog, enable Peripheral Clocks
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_SysCtrl.c file.
//
InitSysCtrl();
//
// Step 2. Initialize GPIO:
// This example function is found in the DSP2833x_Gpio.c file and
// illustrates how to set the GPIO to it's default state.
//
// InitGpio(); // Skipped for this example
//
// For this example use the following configuration
//
Gpio_select();
//
// Step 3. Clear all interrupts and initialize PIE vector table
// Disable CPU interrupts
//
DINT;
//
// Initialize PIE control registers to their default state.
// The default state is all PIE interrupts disabled and flags
// are cleared.
// This function is found in the DSP2833x_PieCtrl.c file.
//
InitPieCtrl();
//
// Disable CPU interrupts and clear all CPU interrupt flags
//
IER = 0x0000;
IFR = 0x0000;
//
// Initialize the PIE vector table with pointers to the shell Interrupt
// Service Routines (ISR).
// This will populate the entire table, even if the interrupt
// is not used in this example. This is useful for debug purposes.
// The shell ISR routines are found in DSP2833x_DefaultIsr.c.
// This function is found in DSP2833x_PieVect.c.
//
InitPieVectTable();
//
// Step 4. Initialize all the Device Peripherals:
// This function is found in DSP2833x_InitPeripherals.c
//
// InitPeripherals(); // Not required for this example
//
// Step 5. User specific code:
//
#if EXAMPLE1
//
// This example uses DATA registers to toggle I/O's
//
Gpio_example1();
#endif // - EXAMPLE1
#if EXAMPLE2
//
// This example uses SET/CLEAR registers to toggle I/O's
//
Gpio_example2();
#endif
#if EXAMPLE3
//
// This example uses TOGGLE registers to toggle I/O's
//
Gpio_example3();
#endif
}
//
// delay_loop -
//
void
delay_loop()
{
volatile long i;
for (i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
}
}
//
// Gpio_example1 -
//
void
Gpio_example1(void)
{
//
// Example 1: Toggle I/Os using DATA registers
//
for(;;)
{
GpioDataRegs.GPADAT.all =0xAAAAAAAA;
GpioDataRegs.GPBDAT.all =0x0000000A;
delay_loop();
GpioDataRegs.GPADAT.all =0x55555555;
GpioDataRegs.GPBDAT.all =0x00000005;
delay_loop();
}
}
//
// Gpio_example2 -
//
void
Gpio_example2(void)
{
//
// Example 2: Toggle I/Os using SET/CLEAR registers
//
for(;;)
{
GpioDataRegs.GPASET.all =0xAAAAAAAA;
GpioDataRegs.GPACLEAR.all =0x55555555;
GpioDataRegs.GPBSET.all =0x0000000A;
GpioDataRegs.GPBCLEAR.all =0x00000005;
delay_loop();
GpioDataRegs.GPACLEAR.all =0xAAAAAAAA;
GpioDataRegs.GPASET.all =0x55555555;
GpioDataRegs.GPBCLEAR.all =0x0000000A;
GpioDataRegs.GPBSET.all =0x00000005;
delay_loop();
}
}
//
// Gpio_example3 -
//
void
Gpio_example3(void)
{
//
// Example 2: Toggle I/Os using TOGGLE registers
//
//
// Set pins to a known state
//
GpioDataRegs.GPASET.all =0xAAAAAAAA;
GpioDataRegs.GPACLEAR.all =0x55555555;
GpioDataRegs.GPBSET.all =0x0000000A;
GpioDataRegs.GPBCLEAR.all =0x00000005;
//
// Use TOGGLE registers to flip the state of the pins.
// Any bit set to a 1 will flip state (toggle)
// Any bit set to a 0 will not toggle.
//
for(;;)
{
GpioDataRegs.GPATOGGLE.all =0xFFFFFFFF;
GpioDataRegs.GPBTOGGLE.all =0x0000000F;
delay_loop();
}
}
//
// Gpio_select -
//
void
Gpio_select(void)
{
EALLOW;
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX1.all = 0x00000000; // All GPIO
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX2.all = 0x00000000; // All GPIO
GpioCtrlRegs.GPAMUX1.all = 0x00000000; // All GPIO
GpioCtrlRegs.GPADIR.all = 0xFFFFFFFF; // All outputs
GpioCtrlRegs.GPBDIR.all = 0x0000000F; // All outputs
EDIS;
}
//
// End of File
//
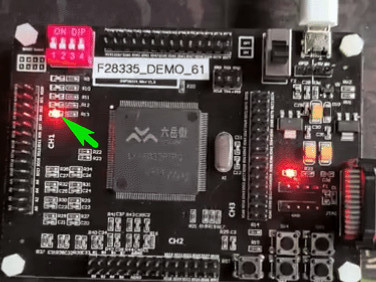
开发资料详见:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1uPuXAdNs4sTFKA5g7uDr4w?pwd=6DSP
本文介绍了六岳微 LY-F335 开发板的相关信息,包括开发板资源、参数特点、主控性能、原理图等,介绍了开发环境搭建的流程以及工程测试方案,为后续开发做好铺垫,也为相关产品的开发设计和应用提供了参考。

 举报
举报


 举报
举报
更多回帖
