前言
openBLT 是开源的小型嵌入式系统bootloader,目前支持ST、NXP、T、InfineonI等多个厂商的ARM、HSC12等内核MCU,非常小巧精致,整体代码整洁规范,下面就从整体上梳理下openBLT。
1 框架
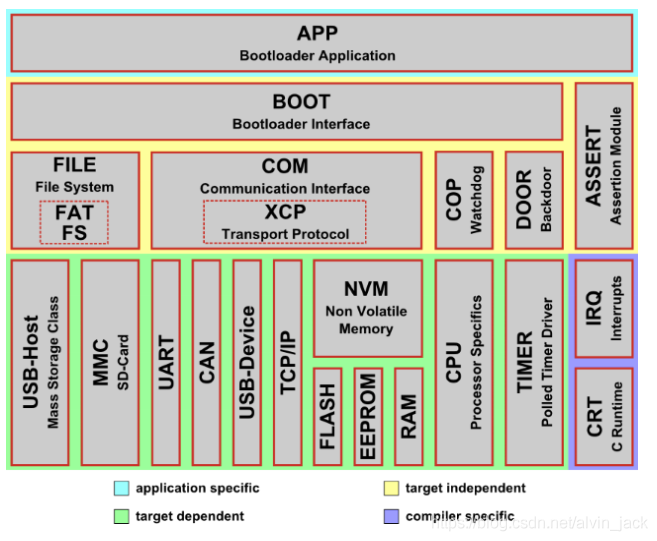
先整体把握一下openBLT的框架,所谓一图胜千言,从上面的图基本就能大概看懂整体系统框架以及实现的机制了。接下来逐个击破。
1.1设备层
设备层是最接近硬件设备的部分,涵盖了在固件升级过程中会使用到的各个硬件接口,如:
通信接口:CAN、ETH、USART、USB、IIC、MMC等
外设模块:TIM、FLASH等
openBLT在设备层针对不同的MCU做了不同的硬件实现,每个硬件接口都做了统一了约定。
CAN底层接口
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/can.h
* brief Bootloader CAN communication interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef CAN_H
#define CAN_H
#if (BOOT_COM_CAN_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void CanInit(void);
void CanTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u len);
blt_bool CanReceivePacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u *len);
#endif /* BOOT_COM_CAN_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* CAN_H */
UART底层接口
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/uart.h
* brief Bootloader UART communication interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef UART_H
#define UART_H
#if (BOOT_COM_UART_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void UartInit(void);
void UartTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u len);
blt_bool UartReceivePacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u *len);
#endif /* BOOT_COM_UART_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* UART_H */
/*********************************** end of uart.h *************************************/
类似的都对设备的硬件接口进行统一了封装,这样做的好处有二:
方便了接下来中间件实现更高一级的功能实现;
实现了中间件与不同硬件MCU的隔离,方便不同平台的移植。
所以这一层的文件下就会有各种各样的板级文件夹,里面实现了不同MCU底层驱动的封装:
.
├── ARM7_LPC2000
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM0_STM32F0
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── Keil
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM0_XMC1
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM3_EFM32
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM3_LM3S
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM3_STM32F1
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── Keil
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM3_STM32F2
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM4_STM32F3
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM4_STM32F4
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM4_STM32L4
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM4_TM4C
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM4_XMC4
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM7_STM32F7
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── HCS12
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── CodeWarrior
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash_ecc.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── TRICORE_TC1798
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ ├── cpu_comp.c
│ │ └── cpu_comp.h
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
1.2中间件
有了设备层的加持,中间件就可以实现更多高级的东西啦,在最开始的框图里面,我们在第二层里面能看到很多的中间件:
COM,负责整个通信数据的收发
硬件层面,CAN、UART、ETH、USB等等;
应用协议,XCP;
COP,看门狗;
DOOR,后门,负责固件跳转、与主机端连接等工作;
FILE,负责实现固件从文件系统(FatFS)中进行更新的逻辑;
Assert,断言检测,出现异常后,保持正常喂看门狗,防止异常程序跑飞;
可以说中间件在设备层的支持下,基本实现了固件数据的获取(CAN、UART、USB、ETH、MMC等)以及固件更新(NVM);
1.2.1 COM
COM主要功能逻辑是通过硬件接口获取数数据、按照既定的协议进行数据的解包和封包,完成整个系统的数据交换;
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/com.h
* brief Bootloader communication interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef COM_H
#define COM_H
#if (BOOT_COM_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Include files
****************************************************************************************/
#include "xcp.h" /* xcp communication layer */
/****************************************************************************************
* Macro definitions
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Defines the maximum number of bytes for transport layer reception
* depending on the activates interface(s).
*/
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (1)
/* update in case CAN interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_CAN_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_CAN_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case UART interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_UART_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_UART_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case USB interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_USB_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_USB_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case NET interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_NET_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_NET_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/** brief Defines the maximum number of bytes for transport layer transmission
* depending on the activates interface(s).
*/
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (1)
/* update in case CAN interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_CAN_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_CAN_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case UART interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_UART_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_UART_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case USB interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_USB_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_USB_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case NET interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_NET_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_NET_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/****************************************************************************************
* Plausibility
****************************************************************************************/
#if (BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA < 1)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (8)
#endif
#if (BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA > 256)
#error "COM.H, BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA cannot be larger than 256."
#endif
#if (BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA < 1)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (8)
#endif
#if (BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA > 65536)
#error "COM.H, BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA cannot be larger than 65536."
#endif
/****************************************************************************************
* Type definitions
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Enumeration for the different communication interfaces. */
typedef enum
{
COM_IF_UART, /**< UART interface */
COM_IF_CAN, /**< CAN interface */
COM_IF_USB, /**< USB interface */
COM_IF_NET, /**< NET interface */
COM_IF_OTHER /**< Other interface */
} tComInterfaceId;
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void ComInit(void);
#if (BOOT_COM_DEFERRED_INIT_ENABLE == 1)
void ComDeferredInit(void);
#endif
void ComTask(void);
void ComFree(void);
blt_int16u ComGetActiveInterfaceMaxRxLen(void);
blt_int16u ComGetActiveInterfaceMaxTxLen(void);
void ComTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int16u len);
blt_bool ComIsConnected(void);
#endif /* BOOT_COM_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* COM_H */
/*********************************** end of com.h **************************************/
/**********************************************************************************//
** brief Updates the communication module by checking if new data was received
** and submitting the request to process newly received data.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void ComTask(void);
主要是完成硬件接口的数据获取(调用设备层通信接口),然后调用XCP接口进行解析
/**********************************************************************************//
** brief Releases the communication module.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void ComFree(void);
调用硬件接口关闭底层通信
/**********************************************************************************//
** brief Transmits the packet using the xcp transport layer.
** param data Pointer to the byte buffer with packet data.
** param len Number of data bytes that need to be transmitted.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void ComTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int16u len)
调用XCP接口进行数据封包
1.2.2 BACKDOOR
Backdoor整体逻辑比较简单,主要判断是否满足程序跳转逻辑。
是否超时
是否与主机建立连接
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/backdoor.h
* brief Bootloader backdoor entry header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef BACKDOOR_H
#define BACKDOOR_H
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void BackDoorInit(void);
void BackDoorCheck(void);
#if (BOOT_BACKDOOR_HOOKS_ENABLE == 0)
void BackDoorSetExtension(blt_int32u extension_ms);
blt_int32u BackDoorGetExtension(void);
void BackDoorRestartTimer(void);
#endif
#endif /* BACKDOOR_H */
/*********************************** end of backdoor.h *********************************/
1.2.3 FILE
file实现固件从文件系统中更新,依赖MMC、USB等设备接口的支持。
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/file.h
* brief Bootloader file system interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef FILE_H
#define FILE_H
#if (BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Include files
****************************************************************************************/
#include "ff.h" /* FATFS file system library */
/****************************************************************************************
* Defines
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Error code for not being able to open the firmware file. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_OPEN_FIRMWARE_FILE (1)
/** brief Error code for not being able to read from the firmware file. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_READ_FROM_FILE (2)
/** brief Error code because in incorrect checksum was found in the firmware file. */
#define FILE_ERROR_INVALID_CHECKSUM_IN_FILE (3)
/** brief Error code because the file pointers read pointer could not be rewinded. */
#define FILE_ERROR_REWINDING_FILE_READ_POINTER (4)
/** brief Error code because an error occurred during the memory erase operation. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_ERASE_MEMORY (5)
/** brief Error code because an error occurred during the memory write operation. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_PROGRAM_MEMORY (6)
/** brief Error code because the program's checksum could not be written to memory. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_WRITE_CHECKSUM (7)
/** brief Maximum number of characters that can be on a line in the firmware file. */
#define MAX_CHARS_PER_LINE (256)
/** brief Maximum number of data bytes that can be on a line in the firmware file
* (S-record).
*/
#define MAX_DATA_BYTES_PER_LINE (MAX_CHARS_PER_LINE/2)
/** brief Return code in case an invalid checksum was detected on an S-record line. */
#define ERROR_SREC_INVALID_CHECKSUM (-1)
/****************************************************************************************
* Type definitions
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Enumeration for the different S-record line types. */
typedef enum
{
LINE_TYPE_S1, /**< 16-bit address line */
LINE_TYPE_S2, /**< 24-bit address line */
LINE_TYPE_S3, /**< 32-bit address line */
LINE_TYPE_UNSUPPORTED /**< unsupported line */
} tSrecLineType;
/** brief Structure type for grouping the parsing results of an S-record line. */
typedef struct
{
blt_char line[MAX_CHARS_PER_LINE]; /**< string buffer for the line chars */
blt_int8u data[MAX_DATA_BYTES_PER_LINE]; /**< array for S1, S2 or S3 data bytes*/
blt_addr address; /**< address on S1, S2 or S3 line */
} tSrecLineParseObject;
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void FileInit(void);
void FileTask(void);
blt_bool FileIsIdle(void);
blt_bool FileHandleFirmwareUpdateRequest(void);
/* functions for reading data from a Motorola S-record file. */
tSrecLineType FileSrecGetLineType(const blt_char *line);
blt_bool FileSrecVerifyChecksum(const blt_char *line);
blt_int16s FileSrecParseLine(const blt_char *line, blt_addr *address, blt_int8u *data);
#endif /* BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* FILE_H */
/*********************************** end of file.h *************************************/
1.3应用层
应用层主要是通过调用各个中间件来实现整个完整openBLT的应用逻辑。
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/boot.h
* brief Bootloader core module header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef BOOT_H
#define BOOT_H
/****************************************************************************************
* Defines
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Main version number of the bootloader core. */
#define BOOT_VERSION_CORE_MAIN (1u)
/** brief Minor version number of the bootloader core. */
#define BOOT_VERSION_CORE_MINOR (8u)
/** brief Patch number of the bootloader core. */
#define BOOT_VERSION_CORE_PATCH (0u)
/****************************************************************************************
* Include files
****************************************************************************************/
/* Note that it is possible to override the standard blt_conf.h configuration header
* file with a project specific one that is defined in the IDE/makefile. For example,
* the following define could be configured: PROJ_BLT_CONF_H="my_boot_config.h". This can
* be handy if you use the bootloader in several projects with a different configuration,
* and enables you to have just one bootloader source base.
*/
#include "types.h" /* variable types */
#include "assert.h" /* assertion checks */
#ifdef PROJ_BLT_CONF_H
#include PROJ_BLT_CONF_H /* custom configuration */
#else
#include "blt_conf.h" /* bootloader configuration */
#endif /* PROJ_BLT_CONF_H */
#include "plausibility.h" /* plausibility checks */
#include "cpu.h" /* cpu driver module */
#include "cop.h" /* watchdog driver module */
#include "nvm.h" /* memory driver module */
#include "timer.h" /* timer driver module */
#include "backdoor.h" /* backdoor entry module */
#include "file.h" /* file system module */
#include "com.h" /* communication interface */
#include "led.h" /* communication interface */
#if (ADDON_GATEWAY_MOD_ENABLE > 0)
#include "gateway.h" /* gateway add-on module */
#endif
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void BootInit(void);
void BootTask(void);
#endif /* BOOT_H */
/*********************************** end of boot.h *************************************/
整个代码运行的功能逻辑入口就在void BootTask(void);
/************************************************************************************//**
** brief Task function of the bootloader core that drives the program.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void BootTask(void)
{
/* service the watchdog */
CopService();
/* update the millisecond timer */
TimerUpdate();
/* update the led */
LedBlinkTask();
#if (BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0)
/* call worker task for updating firmware from locally attached file storage */
FileTask();
#endif /* BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0 */
#if (BOOT_COM_ENABLE > 0)
/* process possibly pending communication data */
ComTask();
#endif
#if (ADDON_GATEWAY_MOD_ENABLE > 0)
/* run the gateway */
GatewayTask();
#endif
/* control the backdoor */
BackDoorCheck();
} /*** end of BootTask ***/
总体来说openBLT的代码层级非常清晰,也很简洁,是一个非常不错的bootloader。
前言
openBLT 是开源的小型嵌入式系统bootloader,目前支持ST、NXP、T、InfineonI等多个厂商的ARM、HSC12等内核MCU,非常小巧精致,整体代码整洁规范,下面就从整体上梳理下openBLT。
1 框架

先整体把握一下openBLT的框架,所谓一图胜千言,从上面的图基本就能大概看懂整体系统框架以及实现的机制了。接下来逐个击破。
1.1设备层
设备层是最接近硬件设备的部分,涵盖了在固件升级过程中会使用到的各个硬件接口,如:
通信接口:CAN、ETH、USART、USB、IIC、MMC等
外设模块:TIM、FLASH等
openBLT在设备层针对不同的MCU做了不同的硬件实现,每个硬件接口都做了统一了约定。
CAN底层接口
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/can.h
* brief Bootloader CAN communication interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef CAN_H
#define CAN_H
#if (BOOT_COM_CAN_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void CanInit(void);
void CanTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u len);
blt_bool CanReceivePacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u *len);
#endif /* BOOT_COM_CAN_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* CAN_H */
UART底层接口
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/uart.h
* brief Bootloader UART communication interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef UART_H
#define UART_H
#if (BOOT_COM_UART_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void UartInit(void);
void UartTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u len);
blt_bool UartReceivePacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int8u *len);
#endif /* BOOT_COM_UART_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* UART_H */
/*********************************** end of uart.h *************************************/
类似的都对设备的硬件接口进行统一了封装,这样做的好处有二:
方便了接下来中间件实现更高一级的功能实现;
实现了中间件与不同硬件MCU的隔离,方便不同平台的移植。
所以这一层的文件下就会有各种各样的板级文件夹,里面实现了不同MCU底层驱动的封装:
.
├── ARM7_LPC2000
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM0_STM32F0
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── Keil
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM0_XMC1
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM3_EFM32
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM3_LM3S
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM3_STM32F1
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── Keil
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM3_STM32F2
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM4_STM32F3
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM4_STM32F4
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM4_STM32L4
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM4_TM4C
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ ├── uart.c
│ └── u***.c
├── ARMCM4_XMC4
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── ARMCM7_STM32F7
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── IAR
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── HCS12
│ ├── can.c
│ ├── CodeWarrior
│ │ └── cpu_comp.c
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash_ecc.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
├── TRICORE_TC1798
│ ├── cpu.c
│ ├── flash.c
│ ├── flash.h
│ ├── GCC
│ │ ├── cpu_comp.c
│ │ └── cpu_comp.h
│ ├── nvm.c
│ ├── target.dox
│ ├── timer.c
│ ├── types.h
│ └── uart.c
1.2中间件
有了设备层的加持,中间件就可以实现更多高级的东西啦,在最开始的框图里面,我们在第二层里面能看到很多的中间件:
COM,负责整个通信数据的收发
硬件层面,CAN、UART、ETH、USB等等;
应用协议,XCP;
COP,看门狗;
DOOR,后门,负责固件跳转、与主机端连接等工作;
FILE,负责实现固件从文件系统(FatFS)中进行更新的逻辑;
Assert,断言检测,出现异常后,保持正常喂看门狗,防止异常程序跑飞;
可以说中间件在设备层的支持下,基本实现了固件数据的获取(CAN、UART、USB、ETH、MMC等)以及固件更新(NVM);
1.2.1 COM
COM主要功能逻辑是通过硬件接口获取数数据、按照既定的协议进行数据的解包和封包,完成整个系统的数据交换;
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/com.h
* brief Bootloader communication interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef COM_H
#define COM_H
#if (BOOT_COM_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Include files
****************************************************************************************/
#include "xcp.h" /* xcp communication layer */
/****************************************************************************************
* Macro definitions
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Defines the maximum number of bytes for transport layer reception
* depending on the activates interface(s).
*/
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (1)
/* update in case CAN interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_CAN_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_CAN_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case UART interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_UART_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_UART_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case USB interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_USB_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_USB_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case NET interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_NET_RX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_NET_RX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/** brief Defines the maximum number of bytes for transport layer transmission
* depending on the activates interface(s).
*/
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (1)
/* update in case CAN interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_CAN_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_CAN_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case UART interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_UART_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_UART_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case USB interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_USB_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_USB_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/* update in case NET interface uses more */
#if (BOOT_COM_NET_TX_MAX_DATA > BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (BOOT_COM_NET_TX_MAX_DATA)
#endif
/****************************************************************************************
* Plausibility
****************************************************************************************/
#if (BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA < 1)
#undef BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA (8)
#endif
#if (BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA > 256)
#error "COM.H, BOOT_COM_TX_MAX_DATA cannot be larger than 256."
#endif
#if (BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA < 1)
#undef BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA
#define BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA (8)
#endif
#if (BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA > 65536)
#error "COM.H, BOOT_COM_RX_MAX_DATA cannot be larger than 65536."
#endif
/****************************************************************************************
* Type definitions
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Enumeration for the different communication interfaces. */
typedef enum
{
COM_IF_UART, /**< UART interface */
COM_IF_CAN, /**< CAN interface */
COM_IF_USB, /**< USB interface */
COM_IF_NET, /**< NET interface */
COM_IF_OTHER /**< Other interface */
} tComInterfaceId;
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void ComInit(void);
#if (BOOT_COM_DEFERRED_INIT_ENABLE == 1)
void ComDeferredInit(void);
#endif
void ComTask(void);
void ComFree(void);
blt_int16u ComGetActiveInterfaceMaxRxLen(void);
blt_int16u ComGetActiveInterfaceMaxTxLen(void);
void ComTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int16u len);
blt_bool ComIsConnected(void);
#endif /* BOOT_COM_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* COM_H */
/*********************************** end of com.h **************************************/
/**********************************************************************************//
** brief Updates the communication module by checking if new data was received
** and submitting the request to process newly received data.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void ComTask(void);
主要是完成硬件接口的数据获取(调用设备层通信接口),然后调用XCP接口进行解析
/**********************************************************************************//
** brief Releases the communication module.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void ComFree(void);
调用硬件接口关闭底层通信
/**********************************************************************************//
** brief Transmits the packet using the xcp transport layer.
** param data Pointer to the byte buffer with packet data.
** param len Number of data bytes that need to be transmitted.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void ComTransmitPacket(blt_int8u *data, blt_int16u len)
调用XCP接口进行数据封包
1.2.2 BACKDOOR
Backdoor整体逻辑比较简单,主要判断是否满足程序跳转逻辑。
是否超时
是否与主机建立连接
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/backdoor.h
* brief Bootloader backdoor entry header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef BACKDOOR_H
#define BACKDOOR_H
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void BackDoorInit(void);
void BackDoorCheck(void);
#if (BOOT_BACKDOOR_HOOKS_ENABLE == 0)
void BackDoorSetExtension(blt_int32u extension_ms);
blt_int32u BackDoorGetExtension(void);
void BackDoorRestartTimer(void);
#endif
#endif /* BACKDOOR_H */
/*********************************** end of backdoor.h *********************************/
1.2.3 FILE
file实现固件从文件系统中更新,依赖MMC、USB等设备接口的支持。
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/file.h
* brief Bootloader file system interface header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef FILE_H
#define FILE_H
#if (BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0)
/****************************************************************************************
* Include files
****************************************************************************************/
#include "ff.h" /* FATFS file system library */
/****************************************************************************************
* Defines
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Error code for not being able to open the firmware file. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_OPEN_FIRMWARE_FILE (1)
/** brief Error code for not being able to read from the firmware file. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_READ_FROM_FILE (2)
/** brief Error code because in incorrect checksum was found in the firmware file. */
#define FILE_ERROR_INVALID_CHECKSUM_IN_FILE (3)
/** brief Error code because the file pointers read pointer could not be rewinded. */
#define FILE_ERROR_REWINDING_FILE_READ_POINTER (4)
/** brief Error code because an error occurred during the memory erase operation. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_ERASE_MEMORY (5)
/** brief Error code because an error occurred during the memory write operation. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_PROGRAM_MEMORY (6)
/** brief Error code because the program's checksum could not be written to memory. */
#define FILE_ERROR_CANNOT_WRITE_CHECKSUM (7)
/** brief Maximum number of characters that can be on a line in the firmware file. */
#define MAX_CHARS_PER_LINE (256)
/** brief Maximum number of data bytes that can be on a line in the firmware file
* (S-record).
*/
#define MAX_DATA_BYTES_PER_LINE (MAX_CHARS_PER_LINE/2)
/** brief Return code in case an invalid checksum was detected on an S-record line. */
#define ERROR_SREC_INVALID_CHECKSUM (-1)
/****************************************************************************************
* Type definitions
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Enumeration for the different S-record line types. */
typedef enum
{
LINE_TYPE_S1, /**< 16-bit address line */
LINE_TYPE_S2, /**< 24-bit address line */
LINE_TYPE_S3, /**< 32-bit address line */
LINE_TYPE_UNSUPPORTED /**< unsupported line */
} tSrecLineType;
/** brief Structure type for grouping the parsing results of an S-record line. */
typedef struct
{
blt_char line[MAX_CHARS_PER_LINE]; /**< string buffer for the line chars */
blt_int8u data[MAX_DATA_BYTES_PER_LINE]; /**< array for S1, S2 or S3 data bytes*/
blt_addr address; /**< address on S1, S2 or S3 line */
} tSrecLineParseObject;
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void FileInit(void);
void FileTask(void);
blt_bool FileIsIdle(void);
blt_bool FileHandleFirmwareUpdateRequest(void);
/* functions for reading data from a Motorola S-record file. */
tSrecLineType FileSrecGetLineType(const blt_char *line);
blt_bool FileSrecVerifyChecksum(const blt_char *line);
blt_int16s FileSrecParseLine(const blt_char *line, blt_addr *address, blt_int8u *data);
#endif /* BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0 */
#endif /* FILE_H */
/*********************************** end of file.h *************************************/
1.3应用层
应用层主要是通过调用各个中间件来实现整个完整openBLT的应用逻辑。
/************************************************************************************//**
* file Source/boot.h
* brief Bootloader core module header file.
* ingroup Core
* internal
*------------------------------------------------------------------------------------*/
#ifndef BOOT_H
#define BOOT_H
/****************************************************************************************
* Defines
****************************************************************************************/
/** brief Main version number of the bootloader core. */
#define BOOT_VERSION_CORE_MAIN (1u)
/** brief Minor version number of the bootloader core. */
#define BOOT_VERSION_CORE_MINOR (8u)
/** brief Patch number of the bootloader core. */
#define BOOT_VERSION_CORE_PATCH (0u)
/****************************************************************************************
* Include files
****************************************************************************************/
/* Note that it is possible to override the standard blt_conf.h configuration header
* file with a project specific one that is defined in the IDE/makefile. For example,
* the following define could be configured: PROJ_BLT_CONF_H="my_boot_config.h". This can
* be handy if you use the bootloader in several projects with a different configuration,
* and enables you to have just one bootloader source base.
*/
#include "types.h" /* variable types */
#include "assert.h" /* assertion checks */
#ifdef PROJ_BLT_CONF_H
#include PROJ_BLT_CONF_H /* custom configuration */
#else
#include "blt_conf.h" /* bootloader configuration */
#endif /* PROJ_BLT_CONF_H */
#include "plausibility.h" /* plausibility checks */
#include "cpu.h" /* cpu driver module */
#include "cop.h" /* watchdog driver module */
#include "nvm.h" /* memory driver module */
#include "timer.h" /* timer driver module */
#include "backdoor.h" /* backdoor entry module */
#include "file.h" /* file system module */
#include "com.h" /* communication interface */
#include "led.h" /* communication interface */
#if (ADDON_GATEWAY_MOD_ENABLE > 0)
#include "gateway.h" /* gateway add-on module */
#endif
/****************************************************************************************
* Function prototypes
****************************************************************************************/
void BootInit(void);
void BootTask(void);
#endif /* BOOT_H */
/*********************************** end of boot.h *************************************/
整个代码运行的功能逻辑入口就在void BootTask(void);
/************************************************************************************//**
** brief Task function of the bootloader core that drives the program.
** return none
**
****************************************************************************************/
void BootTask(void)
{
/* service the watchdog */
CopService();
/* update the millisecond timer */
TimerUpdate();
/* update the led */
LedBlinkTask();
#if (BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0)
/* call worker task for updating firmware from locally attached file storage */
FileTask();
#endif /* BOOT_FILE_SYS_ENABLE > 0 */
#if (BOOT_COM_ENABLE > 0)
/* process possibly pending communication data */
ComTask();
#endif
#if (ADDON_GATEWAY_MOD_ENABLE > 0)
/* run the gateway */
GatewayTask();
#endif
/* control the backdoor */
BackDoorCheck();
} /*** end of BootTask ***/
总体来说openBLT的代码层级非常清晰,也很简洁,是一个非常不错的bootloader。

 举报
举报



 举报
举报

