
FireBeetle 2 ESP32-S3可以使用Arduino IDE、ESP-IDF、MicroPython进行编程,C语言、python都可以轻松的操纵硬件。我选择以vscode为主,插件platformio,需要安装python3.
Purple Pi开发板通过J12排针提供了丰富的GPIO接口,包括UART、SPI、I2C、GPIO等(还包括DC5V、DC3.3V、GND)。
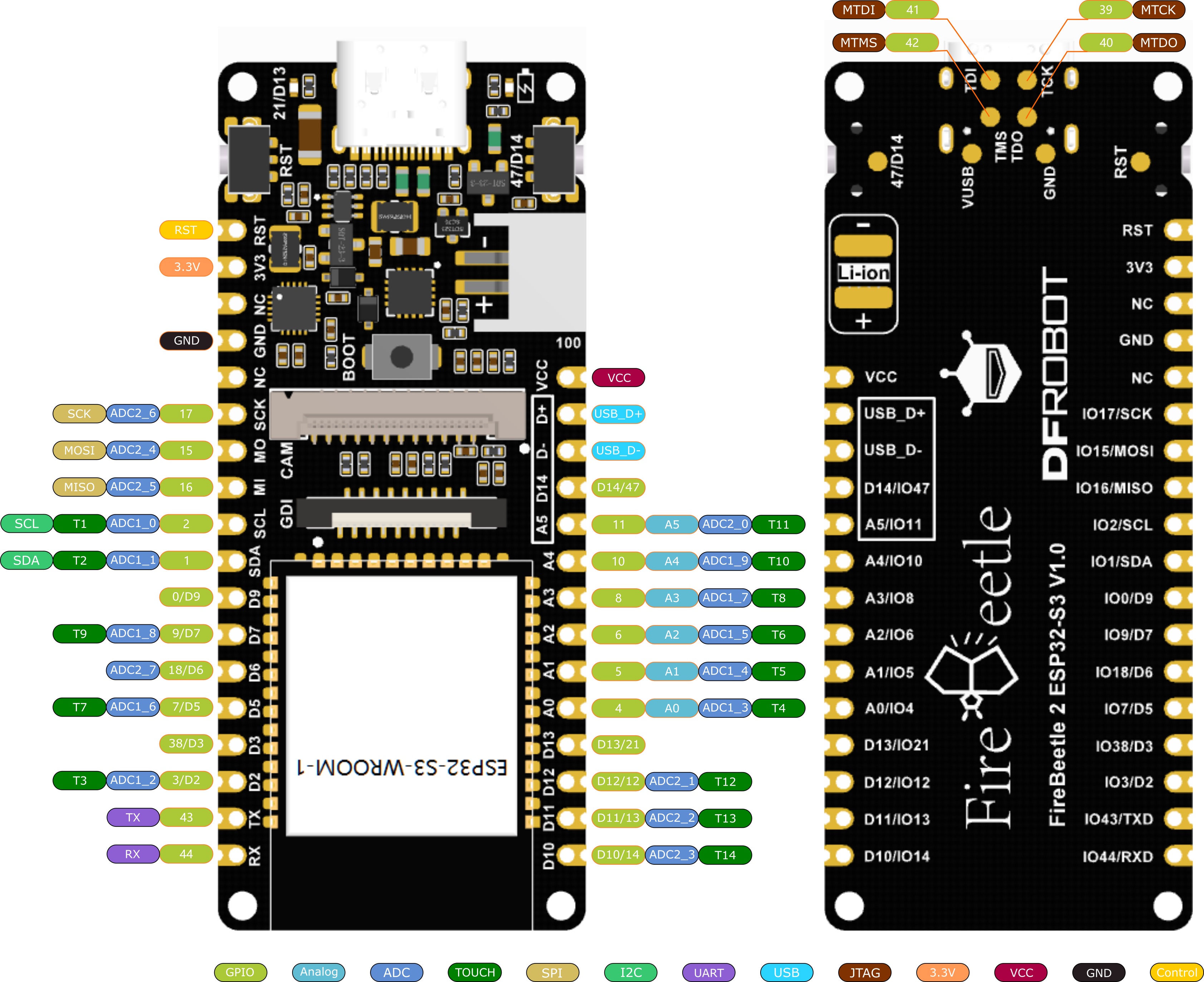
| board | extend |
|---|---|
| IO1/SDA | SSD1306-SDA |
| IO2/SCL | SSD1306-SCK |
| IO7/D5 | DS1302-SCK |
| IO38/D3 | DS1302-DO |
| IO3/D2 | DS1302-RST |
如下图:
在SSD1306上获取实时是指在SSD1306液晶显示屏上显示实时的时间或其它信息。为了实现这一功能,需要通过一个实时时钟(RTC)模块来获取实时的时间,并将时间信息传递给SSD1306液晶显示屏进行显示。
DS1302是一种常用的实时时钟芯片,它具有掉电不丢失时间的特性,即使在掉电的情况下,它仍能保存当前的时间信息。因此,将DS1302与SSD1306结合使用,可以实现在掉电或烧录后仍然能够获取实时时间,并在液晶显示屏上显示。
这样的设计可以使设备具有更好的用户体验,即使在掉电或重新烧录程序的情况下,用户也能看到实时的时间信息,而不需要重新设置时间。这对于一些需要精确时间信息的应用场景是非常有用的,比如钟表、计时器等。
源代码如下:
// CONNECTIONS:
// DS1302 CLK/SCLK --> 7
// DS1302 DAT/IO --> 38
// DS1302 RST/CE --> 3
// DS1302 VCC --> 3.3v - 5v
// DS1302 GND --> GND
// SSD1306 SCK --> IO2/SCL
// SSD1306 SDA --> IO1/SDA
// SSD1306 GND --> GND
// SSD1306 VDD --> 3.3V
#include "OLEDDisplayUi.h"
#include "SSD1306Wire.h"
#include "images.h"
#include <RtcDS1302.h>
#include <TimeLib.h>
#include <Wire.h>
void printDateTime(const RtcDateTime &dt);
#define countof(a) (sizeof(a) / sizeof(a[0]))
ThreeWire myWire(38, 7, 3); // IO, SCLK, CE
SSD1306Wire display(0x3c, SDA, SCL); // IO1 IO2
RtcDS1302<ThreeWire> Rtc(myWire);
OLEDDisplayUi ui(&display);
int screenW = 128;
int screenH = 64;
int clockCenterX = screenW / 2;
int clockCenterY = ((screenH - 16) / 2) + 16; // top yellow part is 16 px height
int clockRadius = 23;
// utility function for digital clock display: prints leading 0
String twoDigits(int digits)
{
if (digits < 10)
{
String i = '0' + String(digits);
return i;
}
else
{
return String(digits);
}
}
void clockOverlay(OLEDDisplay *display, OLEDDisplayUiState *state)
{
}
void analogClockFrame(OLEDDisplay *display, OLEDDisplayUiState *state, int16_t x, int16_t y)
{
// ui.disableIndicator();
// Draw the clock face
// display->drawCircle(clockCenterX + x, clockCenterY + y, clockRadius);
display->drawCircle(clockCenterX + x, clockCenterY + y, 2);
//
// hour ticks
for (int z = 0; z < 360; z = z + 30)
{
// Begin at 0° and stop at 360°
float angle = z;
angle = (angle / 57.29577951); // Convert degrees to radians
int x2 = (clockCenterX + (sin(angle) * clockRadius));
int y2 = (clockCenterY - (cos(angle) * clockRadius));
int x3 = (clockCenterX + (sin(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 8))));
int y3 = (clockCenterY - (cos(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 8))));
display->drawLine(x2 + x, y2 + y, x3 + x, y3 + y);
}
// display second hand
float angle = second() * 6;
angle = (angle / 57.29577951); // Convert degrees to radians
int x3 = (clockCenterX + (sin(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 5))));
int y3 = (clockCenterY - (cos(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 5))));
display->drawLine(clockCenterX + x, clockCenterY + y, x3 + x, y3 + y);
//
// display minute hand
angle = minute() * 6;
angle = (angle / 57.29577951); // Convert degrees to radians
x3 = (clockCenterX + (sin(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 4))));
y3 = (clockCenterY - (cos(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 4))));
display->drawLine(clockCenterX + x, clockCenterY + y, x3 + x, y3 + y);
//
// display hour hand
angle = hour() * 30 + int((minute() / 12) * 6);
angle = (angle / 57.29577951); // Convert degrees to radians
x3 = (clockCenterX + (sin(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 2))));
y3 = (clockCenterY - (cos(angle) * (clockRadius - (clockRadius / 2))));
display->drawLine(clockCenterX + x, clockCenterY + y, x3 + x, y3 + y);
}
void digitalClockFrame(OLEDDisplay *display, OLEDDisplayUiState *state, int16_t x, int16_t y)
{
String timenow = String(hour()) + ":" + twoDigits(minute()) + ":" + twoDigits(second());
display->setTextAlignment(TEXT_ALIGN_CENTER);
display->setFont(ArialMT_Plain_24);
display->drawString(clockCenterX + x, clockCenterY + y, timenow);
}
void printDateTime(const RtcDateTime &dt)
{
char datestring[26];
snprintf_P(datestring,
countof(datestring),
PSTR("%02u/%02u/%04u %02u:%02u:%02u"),
dt.Month(),
dt.Day(),
dt.Year(),
dt.Hour(),
dt.Minute(),
dt.Second());
Serial.print(datestring);
}
void clock_init()
{
Rtc.Begin();
RtcDateTime compiled = RtcDateTime(__DATE__, __TIME__);
printDateTime(compiled);
Serial.println();
if (!Rtc.IsDateTimeValid())
{
// Common Causes:
// 1) first time you ran and the device wasn't running yet
// 2) the battery on the device is low or even missing
Serial.println("RTC lost confidence in the DateTime!");
Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled);
}
if (Rtc.GetIsWriteProtected())
{
Serial.println("RTC was write protected, enabling writing now");
Rtc.SetIsWriteProtected(false);
}
if (!Rtc.GetIsRunning())
{
Serial.println("RTC was not actively running, starting now");
Rtc.SetIsRunning(true);
}
RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime();
if (now < compiled)
{
Serial.println("RTC is older than compile time! (Updating DateTime)");
Rtc.SetDateTime(compiled);
}
else if (now > compiled)
{
Serial.println("RTC is newer than compile time. (this is expected)");
}
else if (now == compiled)
{
Serial.println("RTC is the same as compile time! (not expected but all is fine)");
}
}
// This array keeps function pointers to all frames
// frames are the single views that slide in
FrameCallback frames[] = {analogClockFrame, digitalClockFrame};
// how many frames are there?
int frameCount = 2;
// Overlays are statically drawn on top of a frame eg. a clock
OverlayCallback overlays[] = {clockOverlay};
int overlaysCount = 1;
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(115200);
RtcDateTime now = Rtc.GetDateTime();
Serial.print("compiled: ");
Serial.print(__DATE__);
Serial.println(__TIME__);
// clock function
clock_init(); // init time and date
Serial.println("Init time and date~");
ui.setTargetFPS(60);
// Customize the active and inactive symbol
ui.setActiveSymbol(activeSymbol);
ui.setInactiveSymbol(inactiveSymbol);
// You can change this to
// TOP, LEFT, BOTTOM, RIGHT
ui.setIndicatorPosition(TOP);
// Defines where the first frame is located in the bar.
ui.setIndicatorDirection(LEFT_RIGHT);
// You can change the transition that is used
// SLIDE_LEFT, SLIDE_RIGHT, SLIDE_UP, SLIDE_DOWN
ui.setFrameAnimation(SLIDE_LEFT);
// Add frames
ui.setFrames(frames, frameCount);
// Add overlays
ui.setOverlays(overlays, overlaysCount);
// Initialising the UI will init the display too.
ui.init();
display.flipScreenVertically();
// 从ds1302获取实时
setTime(now.Hour(), now.Minute(), now.Second(), now.Day(), now.Month(), now.Year());
}
void loop()
{
int remainingTimeBudget = ui.update();
if (remainingTimeBudget > 0)
{
delay(remainingTimeBudget);
}
}



更多回帖
