1. ARP 的背景
对于网络世界来说,有 IP 地址就代表了身份。不过在我们常用的网络拓扑类型中,IP 地址并不能准确表达我们的身份。在 ipv4 中牵扯到私有网络地址与子网划分,加上交换机,路由器设备的存在,这些极大扩展了可用的 IP 地址数量,在设备的 MAC 地址与 IP 地址的共同作用下使得更多的设备能连接到网络中。ipv6 拥有极大数量的 IP 地址,同时就没有 ARP 报文,但是会有一个其他类似的功能。
在实际使用中,ARP (Address Resolution Protocol)地址解析协议 就起到了沟通 IP 地址与 MAC 地址的作用。 ARP 的报文比较简单,就是两个功能:ARP request,ARP response;即一个 ARP 查询报文,一个 ARP 回复报文。
学习目标:
掌握 ARP 报文的作用。
掌握 lwip 中 ARP 的实现原理。
掌握 lwip 的 ARP 策略,能简单修改原生逻辑。
2. ARP 报文格式
ARP 报文与 IP 报文都是附着在 ETH 帧之上,可以看到 ARP 报文长度共有 28 字节;包含的内容包括【发送端】与【接收端】的【以太网地址】与【IP 地址】。

以太网目的地址,要发送到的地址,对于不知道的地址,可以全部置为 1;
以太网源地址,也就是发送端的地址;
帧类型 0x0806,表示为 ARP 报文;0x0800 表示 IP 报文;对于 ARP 报文,”帧类型”的实际上与”协议类型”字段是同一个数据;
硬件类型,两个字节, 1 表示硬件地址;当然实际上,“ 0, 2, 3 “都没有太大意义;
协议类型,与帧类型是一致的;在数据填充时,可以把 “协议类型” 拷贝到 “帧类型” 字段;
硬件地址长度,6 个字节,再长也是 6 个字节;
协议地址长度,4个字节,别多想 ipv4 就是 4 个字节,ipv6 也不用这一套;
op,2 个字节; 1 表示 ARP_REQUEST,2 表示 ARP_REPLY;
发送端以太网地址,意义如名称;
发送端 IP 地址,意义如名称;
目的以太网地址,意义如名称,不知道就置空;
目的 IP 地址,意义如名称;
ARP 只有两个报文类型:request 与 response ( reply ) 。
是在知道 IP 地址的基础上,使用 request 查询该 IP 地址可以使用的 MAC 地址,而不是反过来。
一旦收到 ARP 请求,发现该 IP 与本机 IP 地址相符就回复 response ,如果不是就忽略。
为了能维护一个 MAC 与 IP 的映射表,会有一个 ARP 缓存表的存储结构;ETH 帧的收发都会尝试更新这个 ARP 缓存表。
ARP 报文的收发解析的主要功能就是维护这个 ARP 缓存表,以便在发送 IP 报文时可以直接填充 【以太网目的地址】与【以太网源地址】。
3. lwip 对 ARP 功能的实现
根据上述的 ARP 报文,就该意识到有两个比较重要的结构体需要实现:ETH 报文的结构体,以及 ARP 报文的结构体。
/** struct eth_addr and ip4_addr2 */
#define ETH_HWADDR_LEN 6
#define PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(x) x
#define PACK_STRUCT_FLD_8(x) PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(x)
#define PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(x) PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(x)
struct eth_addr {
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_8(u8_t addr[ETH_HWADDR_LEN]);
} PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT;
struct ip4_addr2 {
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t addrw[2]);
} PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT;
/** Ethernet header */
struct eth_hdr {
#if ETH_PAD_SIZE
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_8(u8_t padding[ETH_PAD_SIZE]);
#endif
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(struct eth_addr dest);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(struct eth_addr src);
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t type);
} PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT;
/** the ARP message, see RFC 826 ("Packet format") */
struct etharp_hdr {
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t hwtype);
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t proto);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_8(u8_t hwlen);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_8(u8_t protolen);
PACK_STRUCT_FIELD(u16_t opcode);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(struct eth_addr shwaddr);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(struct ip4_addr2 sipaddr);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(struct eth_addr dhwaddr);
PACK_STRUCT_FLD_S(struct ip4_addr2 dipaddr);
} PACK_STRUCT_STRUCT;
以上的结构是为了能方便得按照报文格式来填充数据,还需要一个用来管理 ARP 映射表的结构;
/** struct for queueing outgoing packets for unknown address
* defined here to be accessed by memp.h
*/
struct etharp_q_entry {
struct etharp_q_entry *next;
struct pbuf *p;
};
struct etharp_entry {
#if ARP_QUEUEING
/** Pointer to queue of pending outgoing packets on this ARP entry. */
struct etharp_q_entry *q;
#else /* ARP_QUEUEING */
/** Pointer to a single pending outgoing packet on this ARP entry. */
struct pbuf *q;
#endif /* ARP_QUEUEING */
ip4_addr_t ipaddr;
struct netif *netif;
struct eth_addr ethaddr;
u16_t ctime;
u8_t state;
};
static struct etharp_entry arp_table[ARP_TABLE_SIZE];
OK,描述到这里,lwip 对 ARP 报文的支持所需要的基础数据结构已经完备了;但是除了数据结构,也应当有对应的算法才能实现 TCP/IP 所要求的规范,即实现 ARP 程序。我们先不看具体实现,先通过我们上面对 ARP 功能的描述,先猜测一下应该需要什么功能:
发送数据时,根据 ARP 表填充 ETH 帧的地址。
如果 ARP 表没有对应的 IP 与 MAC 地址的条目,应当发送 ARP request 来查询。
在收到 ARP response 时,应当把报文中的 IP 与 MAC 地址添加到 ARP表中。
应当提供一个查询 ARP 表的功能,并能更新 ARP 映射关系。
3.1 lwip 的 ARP 缓存表维护
上面的函数已经能完成对 ARP 数据包的发送,解析,查找功能;因为一个网络中,设备不可能是一直都不会变的。比如 DHCP 给你分配了一个 IP ,在你不使用后会收回这些资源,也许会分配给其他人;也就是说,IP 与 MAC 的对应关系,是会随着时间改变而改变的。因此,lwip 维护的 ARP 表是需要频繁更新的。
而为了表示 ARP 缓存表中,IP 与 ARP 的对应关系(后面称为一个表项),每个表项都会有个 state 来表示状态,也就是上面的 u8 state 字段。lwip 定义的表项状态共有 6 种,当然是在你支持静态 ARP 映射表的情况下。
/** ARP states */
enum etharp_state {
ETHARP_STATE_EMPTY = 0, /* 空表 */
ETHARP_STATE_PENDING, /* 只记录了 IP ,而没有记录 MAC,一般是发送了 arp_request 的短暂状态 */
ETHARP_STATE_STABLE, /* 记录了 IP 和 MAC */
ETHARP_STATE_STABLE_REREQUESTING_1, /* stable 状态下,ctime 继续增大引发广播或者单播一个 arp_request ,并置为 REREQUESTING_1 */
ETHARP_STATE_STABLE_REREQUESTING_2 /* 已经发送了 arp_request 但是没有回复,会从 REREQUESTING_1 置为 REREQUESTING_2 */
#if ETHARP_SUPPORT_STATIC_ENTRIES
,ETHARP_STATE_STATIC /* 静态表,不会别 ARP 管理修改的条目 */
#endif /* ETHARP_SUPPORT_STATIC_ENTRIES */
};
这些表项的状态,都会影响 ARP 缓存表的更新;而更新策略与上面的一些函数的执行逻辑有关,比较重要的逻辑是:
pending 状态下,对应的 pbuf 不会被发出,只有 >= stable 才会被发出。
pending 状态下,ctime 超时会直接导致条目被删除,置为 empty。
stable 状态下, ctime 超时会被字节置为 pending 。
stable 状态下,会定时检查 ctime ,在达到一定阀值时会通过广播或者单播发送一个 arp_request,并被置为 rerequesting_1 状态。
在 arp_tmr 触发时,如果已经为 rerequesting_1 状态,会被置为 rerequesting_2。
rerequesting_1 与 rerequesting_2 到底什么意义:避免连续(指在多次)发送 arp_request 而设计的,也许是怕网络环境干扰。
3.2 lwip 提供的 ARP 功能函数
我们通过分析已经获悉,ARP 程序肯定要具备上述 4 种功能;不过,在 Lwip 的实际实现中,肯定不止这 4 种基础功能,肯定要有更多的函数来实现这个目的。关于 lwip 的 ARP 内容的代码,是存放在 lwip/src/core/ipv4/etharp.c 中。
为了梳理 ARP 的功能,我们选择其中的 5 个函数来学习 lwip 的 ARP 功能实现:
/* 查找 ARP 映射表中 ipaddr 条目,并返回相对位置 */
static s8_t etharp_find_entry(const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr, u8_t flags, struct netif* netif);
/* 尝试发送 IP 数据包, 单播,多播或者广播数据 */
err_t etharp_output(struct netif *netif, struct pbuf *q, const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr);
/* 查询 ARP 表,不存在则调用 etharp_request 获取,存在则发送数据 */
err_t etharp_query(struct netif *netif, const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr, struct pbuf *q);
/* 尝试发送 ARP 请求数据包 */
err_t etharp_request(struct netif *netif, const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr);
/* 解析 ARP 数据包 */
void etharp_input(struct pbuf *p, struct netif *netif);
其中,最难以理解得是 etharp_find_entry 与 etharp_query 函数,对于这两个函数我们主要分析其意义;剩下的 3 个函数,我们则具体看看代码的实现。通过这 5 个比较有代表性的函数,我们来理解一个表项中的 state ,ctime,p 这些值究竟怎样影响整个 ARP 报文的发送与解析策略。
3.2.1 函数 etharp_find_entry
该函数位于 lwip/src/core/ipv4/etharp.c 中,这个函数的作用可以通过注释来描述:
/**
* Search the ARP table for a matching or new entry.
*
* If an IP address is given, return a pending or stable ARP entry that matches
* the address. If no match is found, create a new entry with this address set,
* but in state ETHARP_EMPTY. The caller must check and possibly change the
* state of the returned entry.
*
* If ipaddr is NULL, return a initialized new entry in state ETHARP_EMPTY.
*
* In all cases, attempt to create new entries from an empty entry. If no
* empty entries are available and ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD flag is set, recycle
* old entries. Heuristic choose the least important entry for recycling.
*
* @param ipaddr IP address to find in ARP cache, or to add if not found. * @param flags See @ref etharp_state * @param netif netif related to this address (used for NETIF_HWADDRHINT)
*
* @Return The ARP entry index that matched or is created, ERR_MEM if no * entry is found or could be recycled.
*/
通过上面的描述,我们能知道 etharp_find_entry 的策略如下:
如果参数中 IP 地址被给定,则返回一个 stable 或者 pending 状态的表项;
如果 IP 地址被给定,但是没有处于 stable 或者 pending 状态的表项,则会找一个 empty 的表项并返回;
如果 IP 地址为空,则会创建一个 empty 的表项并返回;
如果很不巧,ARP 表中没有处于 empty 的表项;在 flag 为 ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD 的情况下,找一个最不重要的表项置空并返回;
ETHARP_FLAG_FIND_ONLY 与 ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD 的区别,就是前者尽量找到一个表项;后者必须找到一个表项(哪怕是清空之前已经存在的);
上面的函数描述中有一个黑洞,ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD 必须找到一个表项,哪怕是通过回收一个最不重要的表项的方式;那最不重要的表项是什么表项呢,我们可以一起看看代码
/* b) choose the least destructive entry to recycle: // 1 -> 4, 优先级就是这样
* 1) empty entry
* 2) oldest stable entry
* 3) oldest pending entry without queued packets
* 4) oldest pending entry with queued packets
*
* { ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD is set at this point }
*/
/* 1) empty entry available? */
if (empty < ARP_TABLE_SIZE) {
i = empty;
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_find_entry: selecting empty entry %"U16_F"
", (u16_t)i));
} else {
/* 2) found recyclable stable entry? */
if (old_stable < ARP_TABLE_SIZE) {
/* recycle oldest stable*/
i = old_stable;
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_find_entry: selecting oldest stable entry %"U16_F"
", (u16_t)i));
/* no queued packets should exist on stable entries */
LWIP_ASSERT("arp_table.q == NULL", arp_table.q == NULL);
/* 3) found recyclable pending entry without queued packets? */
} else if (old_pending < ARP_TABLE_SIZE) {
/* recycle oldest pending */
i = old_pending;
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_find_entry: selecting oldest pending entry %"U16_F" (without queue)
", (u16_t)i));
/* 4) found recyclable pending entry with queued packets? */
} else if (old_queue < ARP_TABLE_SIZE) {
/* recycle oldest pending (queued packets are free in etharp_free_entry) */
i = old_queue;
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_find_entry: selecting oldest pending entry %"U16_F", freeing packet queue %p
", (u16_t)i, (void *)(arp_table.q)));
/* no empty or recyclable entries found */
} else {
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_find_entry: no empty or recyclable entries found
"));
return (s8_t)ERR_MEM;
}
/* { empty or recyclable entry found } */
LWIP_ASSERT("i < ARP_TABLE_SIZE", i < ARP_TABLE_SIZE);
etharp_free_entry(i);
}
我在这里解释一下,为什么会是 1->4 这个顺序:
空表项与最老的 state 最先被使用的原因,就是因为 ARP 表是需要随时更新的,太老的表项可能本身就是错误的或者过时的,因此先删除是没有问题的。
处于 pending 状态且没有待发送数据的表项与处于 pending 状态但是有待发送数据的表项相比;有待发送数据的表项上挂载了一些数据,有可能是 PING 命令之类或者其他的数据,删除这些是比较危险的;而没有待发送数据的表项就没有这个顾虑。
3.2.2 函数 etharp_query
该函数位于 lwip/src/core/ipv4/etharp.c 中,这个函数其实是一些策略的合集:
/**
* Send an ARP request for the given IP address and/or queue a packet.
*
* If the IP address was not yet in the cache, a pending ARP cache entry
* is added and an ARP request is sent for the given address. The packet
* is queued on this entry.
*
* If the IP address was already pending in the cache, a new ARP request
* is sent for the given address. The packet is queued on this entry.
*
* If the IP address was already stable in the cache, and a packet is
* given, it is directly sent and no ARP request is sent out.
*
* If the IP address was already stable in the cache, and no packet is
* given, an ARP request is sent out.
*
* @param netif The lwIP network interface on which ipaddr
* must be queried for.
* @param ipaddr The IP address to be resolved.
* @param q If non-NULL, a pbuf that must be delivered to the IP address.
* q is not freed by this function.
*
* @NOTE q must only be ONE packet, not a packet queue! *
* @return
* - ERR_BUF Could not make room for Ethernet header.
* - ERR_MEM Hardware address unknown, and no more ARP entries available
* to query for address or queue the packet.
* - ERR_MEM Could not queue packet due to memory shortage.
* - ERR_RTE No route to destination (no gateway to external networks).
* - ERR_ARG Non-unicast address given, those will not appear in ARP cache.
*
*/
其实,顺着代码看下来,策略也很清晰:
如果不能找到表项,那没有办法,只能一个新的 empty 表项,发送一个 arp_request 并置为 pending;如果 pbuf 中有数据继续执行,没有直接返回。
如果找到表项,那最好,直接发送数据就行了(这里指真实的 IP 数据,而不是 ARP 数据),然后返回。
如果处于 pending 状态(其实走到这一步,empty 也已经是 pending 了),而且 pbuf 中有数据,那就挂载了对应的 pbuf 链表上,等待发送;这里有一些拷贝的动作,只要 pbuf 链表中有不是 PBUF_ROM 的的节点,整个 pbuf 数据都需要拷贝到新的数据链中,谨防被意外修改。
3.2.3 函数 etharp_request
const struct eth_addr ethbroadcast = {{0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff,0xff}};
const struct eth_addr ethzero = {{0,0,0,0,0,0}};
/**
* Send a raw ARP packet (opcode and all addresses can be modified)
*
* @param netif the lwip network interface on which to send the ARP packet
* @param ethsrc_addr the source MAC address for the ethernet header
* @param ethdst_addr the destination MAC address for the ethernet header
* @param hwsrc_addr the source MAC address for the ARP protocol header
* @param ipsrc_addr the source IP address for the ARP protocol header
* @param hwdst_addr the destination MAC address for the ARP protocol header
* @param ipdst_addr the destination IP address for the ARP protocol header
* @param opcode the type of the ARP packet
* @return ERR_OK if the ARP packet has been sent
* ERR_MEM if the ARP packet couldn't be allocated
* any other err_t on failure
*/
static err_t
etharp_raw(struct netif *netif, const struct eth_addr *ethsrc_addr,
const struct eth_addr *ethdst_addr,
const struct eth_addr *hwsrc_addr, const ip4_addr_t *ipsrc_addr,
const struct eth_addr *hwdst_addr, const ip4_addr_t *ipdst_addr,
const u16_t opcode);
/**
* Send an ARP request packet asking for ipaddr to a specific eth address.
* Used to send unicast request to refresh the ARP table just before an entry
* times out
*
* @param netif the lwip network interface on which to send the request
* @param ipaddr the IP address for which to ask
* @param hw_dst_addr the ethernet address to send this packet to
* @return ERR_OK if the request has been sent
* ERR_MEM if the ARP packet couldn't be allocated
* any other err_t on failure
*/
static err_t
etharp_request_dst(struct netif *netif, const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr, const struct eth_addr* hw_dst_addr)
{
return etharp_raw(netif, (struct eth_addr *)netif->hwaddr, hw_dst_addr,
(struct eth_addr *)netif->hwaddr, netif_ip4_addr(netif), ðzero,
ipaddr, ARP_REQUEST);
}
/**
* Send an ARP request packet asking for ipaddr.
*
* @param netif the lwip network interface on which to send the request
* @param ipaddr the IP address for which to ask
* @return ERR_OK if the request has been sent
* ERR_MEM if the ARP packet couldn't be allocated
* any other err_t on failure
*/
err_t
etharp_request(struct netif *netif, const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr)
{
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_request: sending ARP request.
"));
return etharp_request_dst(netif, ipaddr, ðbroadcast);
}
etharp_request 已经是一个功能函数了,功能函数就表明很容易看懂。OK,我们看看到底干了什么。
首先 eth 帧的广播地址是全 1 的,再使用 etharp_raw 函数发送时,arp 协议中的 hw 字段,全部设置为 0;这里是协议要求,无可厚非。
可以看到 lwip 这里确实是发送了一个 arp_request 的数据包出去。
3.2.4 函数 etharp_input
/**
* Responds to ARP requests to us. Upon ARP replies to us, add entry to cache
* send out queued IP packets. Updates cache with snooped address pairs.
*
* Should be called for incoming ARP packets. The pbuf in the argument
* is freed by this function.
*
* @param p The ARP packet that arrived on netif. Is freed by this function.
* @param netif The lwIP network interface on which the ARP packet pbuf arrived.
*
* @see pbuf_free()
*/
void
etharp_input(struct pbuf *p, struct netif *netif)
{
struct etharp_hdr *hdr;
/* these are aligned properly, whereas the ARP header fields might not be */
ip4_addr_t sipaddr, dipaddr;
u8_t for_us;
LWIP_ERROR("netif != NULL", (netif != NULL), return;);
hdr = (struct etharp_hdr *)p->payload;
/* RFC 826 "Packet Reception": */
if ((hdr->hwtype != PP_HTONS(HWTYPE_ETHERNET)) ||
(hdr->hwlen != ETH_HWADDR_LEN) ||
(hdr->protolen != sizeof(ip4_addr_t)) ||
(hdr->proto != PP_HTONS(ETHTYPE_IP))) {
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE | LWIP_DBG_LEVEL_WARNING,
("etharp_input: packet dropped, wrong hw type, hwlen, proto, protolen or ethernet type (%"U16_F"/%"U16_F"/%"U16_F"/%"U16_F")
",
hdr->hwtype, (u16_t)hdr->hwlen, hdr->proto, (u16_t)hdr->protolen));
ETHARP_STATS_INC(etharp.proterr);
ETHARP_STATS_INC(etharp.drop);
pbuf_free(p);
return;
}
ETHARP_STATS_INC(etharp.recv);
#if LWIP_AUTOIP
/* We have to check if a host already has configured our random
* created link local address and continuously check if there is
* a host with this IP-address so we can detect collisions */
autoip_arp_reply(netif, hdr);
#endif /* LWIP_AUTOIP */
/* Copy struct ip4_addr2 to aligned ip4_addr, to support compilers without
* structure packing (not using structure copy which breaks strict-aliasing rules). */
IPADDR2_COPY(&sipaddr, &hdr->sipaddr);
IPADDR2_COPY(&dipaddr, &hdr->dipaddr);
/* this interface is not configured? */
if (ip4_addr_isany_val(*netif_ip4_addr(netif))) {
for_us = 0;
} else {
/* ARP packet directed to us? */
for_us = (u8_t)ip4_addr_cmp(&dipaddr, netif_ip4_addr(netif));
}
/* ARP message directed to us?
-> add IP address in ARP cache; assume requester wants to talk to us,
can result in directly sending the queued packets for this host.
ARP message not directed to us?
-> update the source IP address in the cache, if present */
etharp_update_arp_entry(netif, &sipaddr, &(hdr->shwaddr),
for_us ? ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD : ETHARP_FLAG_FIND_ONLY);
/* now act on the message itself */
switch (hdr->opcode) {
/* ARP request? */
case PP_HTONS(ARP_REQUEST):
/* ARP request. If it asked for our address, we send out a
* reply. In any case, we time-stamp any existing ARP entry,
* and possibly send out an IP packet that was queued on it. */
LWIP_DEBUGF (ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_input: incoming ARP request
"));
/* ARP request for our address? */
if (for_us) {
/* send ARP response */
etharp_raw(netif,
(struct eth_addr *)netif->hwaddr, &hdr->shwaddr,
(struct eth_addr *)netif->hwaddr, netif_ip4_addr(netif),
&hdr->shwaddr, &sipaddr,
ARP_REPLY);
/* we are not configured? */
} else if (ip4_addr_isany_val(*netif_ip4_addr(netif))) {
/* { for_us == 0 and netif->ip_addr.addr == 0 } */
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_input: we are unconfigured, ARP request ignored.
"));
/* request was not directed to us */
} else {
/* { for_us == 0 and netif->ip_addr.addr != 0 } */
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_input: ARP request was not for us.
"));
}
break;
case PP_HTONS(ARP_REPLY):
/* ARP reply. We already updated the ARP cache earlier. */
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_input: incoming ARP reply
"));
#if (LWIP_DHCP && DHCP_DOES_ARP_CHECK)
/* DHCP wants to know about ARP replies from any host with an
* IP address also offered to us by the DHCP server. We do not
* want to take a duplicate IP address on a single network.
* @todo How should we handle redundant (fail-over) interfaces? */
dhcp_arp_reply(netif, &sipaddr);
#endif /* (LWIP_DHCP && DHCP_DOES_ARP_CHECK) */
break;
default:
LWIP_DEBUGF(ETHARP_DEBUG | LWIP_DBG_TRACE, ("etharp_input: ARP unknown opcode type %"S16_F"
", lwip_htons(hdr->opcode)));
ETHARP_STATS_INC(etharp.err);
break;
}
/* free ARP packet */
pbuf_free(p);
}
可以看到,一旦 ARP 报文到达,都会被这个函数所判断执行;逻辑是这样的:
如果收到的是给自己的 ARP request ,就回复一个 ARP reply 报文;如果不是给自己的,记录一些有用 ARP 的信息后,就忽略掉。
如果是给自己的 ARP reply 报文,会有一些逻辑与 DHCP 过程有关,可以在 DHCP 章节查看。
3.2.5 函数 etharp_output
/**
* Resolve and fill-in Ethernet address header for outgoing IP packet.
*
* For IP multicast and broadcast, corresponding Ethernet addresses
* are selected and the packet is transmitted on the link.
*
* For unicast addresses, the packet is submitted to etharp_query(). In
* case the IP address is outside the local network, the IP address of
* the gateway is used.
*
* @param netif The lwIP network interface which the IP packet will be sent on.
* @param q The pbuf(s) containing the IP packet to be sent.
* @param ipaddr The IP address of the packet destination.
*
* @return
* - ERR_RTE No route to destination (no gateway to external networks),
* or the return type of either etharp_query() or ethernet_output().
*/
err_t
etharp_output(struct netif *netif, struct pbuf *q, const ip4_addr_t *ipaddr)
{
const struct eth_addr *dest;
struct eth_addr mcastaddr;
const ip4_addr_t *dst_addr = ipaddr;
LWIP_ASSERT("netif != NULL", netif != NULL);
LWIP_ASSERT("q != NULL", q != NULL);
LWIP_ASSERT("ipaddr != NULL", ipaddr != NULL);
/* Determine on destination hardware address. Broadcasts and multicasts
* are special, other IP addresses are looked up in the ARP table. */
/* broadcast destination IP address? */
if (ip4_addr_isbroadcast(ipaddr, netif)) {
/* broadcast on Ethernet also */
dest = (const struct eth_addr *)ðbroadcast;
/* multicast destination IP address? */
} else if (ip4_addr_ismulticast(ipaddr)) {
/* Hash IP multicast address to MAC address.*/
mcastaddr.addr[0] = LL_IP4_MULTICAST_ADDR_0;
mcastaddr.addr[1] = LL_IP4_MULTICAST_ADDR_1;
mcastaddr.addr[2] = LL_IP4_MULTICAST_ADDR_2;
mcastaddr.addr[3] = ip4_addr2(ipaddr) & 0x7f;
mcastaddr.addr[4] = ip4_addr3(ipaddr);
mcastaddr.addr[5] = ip4_addr4(ipaddr);
/* destination Ethernet address is multicast */
dest = &mcastaddr;
/* unicast destination IP address? */
} else {
s8_t i;
/* outside local network? if so, this can neither be a global broadcast nor
a subnet broadcast. */
if (!ip4_addr_netcmp(ipaddr, netif_ip4_addr(netif), netif_ip4_netmask(netif)) &&
!ip4_addr_islinklocal(ipaddr)) {
#if LWIP_AUTOIP
struct ip_hdr *iphdr = LWIP_ALIGNMENT_CAST(struct ip_hdr*, q->payload);
/* According to RFC 3297, chapter 2.6.2 (Forwarding Rules), a packet with
a link-local source address must always be "directly to its destination
on the same physical link. The host MUST NOT send the packet to any
router for forwarding". */
if (!ip4_addr_islinklocal(&iphdr->src))
#endif /* LWIP_AUTOIP */
{
#ifdef LWIP_HOOK_ETHARP_GET_GW
/* For advanced routing, a single default gateway might not be enough, so get
the IP address of the gateway to handle the current destination address. */
dst_addr = LWIP_HOOK_ETHARP_GET_GW(netif, ipaddr);
if (dst_addr == NULL)
#endif /* LWIP_HOOK_ETHARP_GET_GW */
{
/* interface has default gateway? */
if (!ip4_addr_isany_val(*netif_ip4_gw(netif))) {
/* send to hardware address of default gateway IP address */
dst_addr = netif_ip4_gw(netif);
/* no default gateway available */
} else {
/* no route to destination error (default gateway missing) */
return ERR_RTE;
}
}
}
}
#if LWIP_NETIF_HWADDRHINT
if (netif->addr_hint != NULL) {
/* per-PCB cached entry was given */ u8_t etharp_cached_entry = *(netif->addr_hint);
if (etharp_cached_entry < ARP_TABLE_SIZE) {
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_HWADDRHINT */
if ((arp_table[etharp_cached_entry].state >= ETHARP_STATE_STABLE) &&
#if ETHARP_TABLE_MATCH_NETIF
(arp_table[etharp_cached_entry].netif == netif) &&
#endif
(ip4_addr_cmp(dst_addr, &arp_table[etharp_cached_entry].ipaddr))) {
/* the per-pcb-cached entry is stable and the right one! */
ETHARP_STATS_INC(etharp.cachehit);
return etharp_output_to_arp_index(netif, q, etharp_cached_entry);
}
#if LWIP_NETIF_HWADDRHINT
}
}
#endif /* LWIP_NETIF_HWADDRHINT */
/* find stable entry: do this here since this is a critical path for
throughput and etharp_find_entry() is kind of slow */
for (i = 0; i < ARP_TABLE_SIZE; i++) {
if ((arp_table.state >= ETHARP_STATE_STABLE) &&
#if ETHARP_TABLE_MATCH_NETIF
(arp_table.netif == netif) &&
#endif
(ip4_addr_cmp(dst_addr, &arp_table.ipaddr))) {
/* found an existing, stable entry */
ETHARP_SET_HINT(netif, i);
return etharp_output_to_arp_index(netif, q, i);
}
}
/* no stable entry found, use the (slower) query function:
queue on destination Ethernet address belonging to ipaddr */
return etharp_query(netif, dst_addr, q);
}
/* continuation for multicast/broadcast destinations */
/* obtain source Ethernet address of the given interface */
/* send packet directly on the link */
return ethernet_output(netif, q, (struct eth_addr*)(netif->hwaddr), dest, ETHTYPE_IP);
}
这个函数会被 IP 层的输出函数直接调用以发送数据;IP 层的数据会有广播,多播,单播的数据,所以在该函数中,处理方式也是不一样的。
对于 IP 地址是广播地址的,eth 的地址也要设置为广播;
对于 IP 地址是多播地址的,eth 的地址也要设置为多播;
对于 IP 地址是单播地址且本网段内的,那直接继续下一步的操作;
对于 IP 地址是单播地址但不是本网段的,也就是需要路由器的转发,eth 的地址要设置为网关的地址;
etharp_cached_entry 的作用应该是加快处理速度,如果连续的数据发送,每次发送都要检索一边 arp 表会比较浪费;cached 的参与可以明显提供速度。
如果是 ARP 缓存表中找不到表项,那啥也别说了,调用 etharp_query 挂载起来吧,等待后面有机会再发送吧。
3.3 ARP / IP 报文在 lwip 中的流向
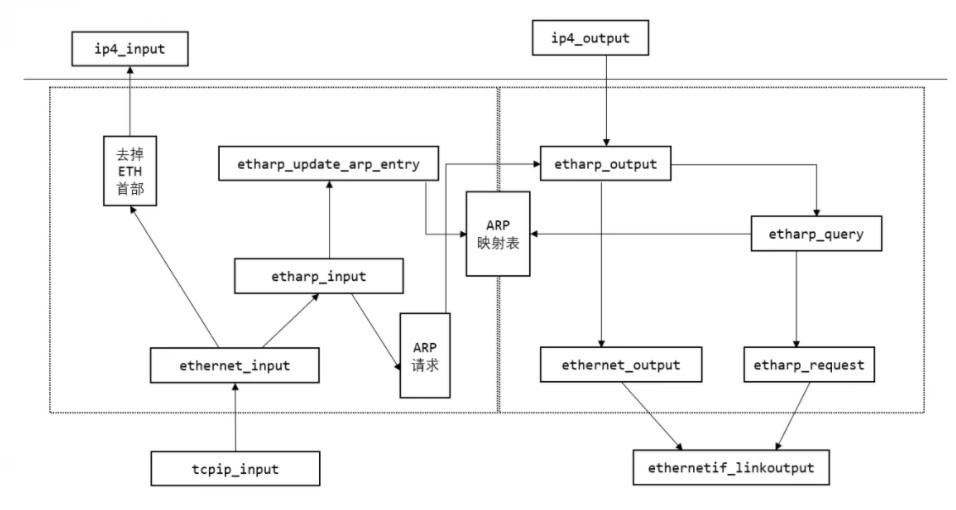
通过上面的函数,我们能大概了解具体的 ARP 功能的实现;对于 IP 数据包在整个 lwip 的流向,可以通过下面这个图来了解。在看图之前,还需要理解在 lwip 提供的三个接口:
IP 报文输入接口:tcpip_input
IP 报文的输出接口:netif->output = etharp_output
ETH 帧的输出接口:netif->linkoutput = ethernetif_linkoutput;
 4. 拓展
4. 拓展4.1 ARP 攻击的原理
名字听起来很厉害,实际上就是通过 ARP 报文来达到干扰服务的目的。ARP 的报文可以使得设备不能正常发送 IP 数据。
欺骗,劫持,基本是属于一类;如果你把该发往别人的 IP 地址的 ETH 帧拿走,就要在别人的机器里将对应的 ARP 缓存换为你的。这样的话,别人的设备可能就会有断网,丢包的现象;毕竟,你这都没有提供服务,别人不掉线才怪。
DOS 攻击,也是一类;这基本是属于纯属的瘫痪手段,让设备只能处理 ARP 报文而忽略其他的报文来达到这个目的。
当然还有些更新型,更加巧妙的攻击方式;但是攻击的原理,都是依赖于 ARP 的 request 与 reply 功能。
4.2 IPv6 如何处置 IPv4 的 APR 功能
ipv6 没有 ARP 协议,但是为了实现类似的效果;ipv6 拥有 NDP (Neighbor Discovery Protocol) 协议,这是 ARP 与 ICMP 的集合。
4.3 ARP,IP,ICMP,IGMP,UDP,TCP,User Data 在 ETH 帧上的关系
ETH 是最底层的层级;
ARP 和 IP 是同一个层级的;
ICMP,IGMP,UDP,TCP 是同一个层级的;
User Data 是最上层的层级,MQTT,HTTP 这些都属于这一层;

从图片上可以看出来,每一层的具体范围;以太网帧指得就是 ETH 帧。4.4 Wireshark 抓取标准 ARP 报文
开发板使用 ETH 的方式接入交换机,选用 lwip 2.0.2 的协议栈,可以使用 RT-Thread 的自动配置功能;在虚拟机上搭一个 ubuntu 的平台,安装上 wireshark ,把网卡的驱动都安装好,就可以开始抓取 ARP 报文了。 开发板 : IP: 192.168.12.107 MAC:00 80 e1 0f 54 46
Ubuntu: IP: 192.168.12.200 MAC:00 0c 29 fa e3 4c
ARP 的报文,在一个比较大的网络中,比如公司网络中可能会比较多;可以取个巧办法,不以 arp 的条件筛选报文,而使用 eth 的条件筛选。这样的话,无论是 ARP,DHCP 还是其他的什么报文,都可以抓上。如图所示:
这是一个 request 报文,比如,在启动开发板使用 ping 命令来 ping 我们的 ubuntu 平台,抓出的信息被圈起来了。

可以看到 ETH 帧的 dst 地址是广播地址全为1;而内部的 ARP 报文的 Target mac ( dst ) 的地址则全为0;这个抓包同我们上面的分析是一致的。这是一个 reply 报文,开发板向 ubuntu 平台发送 ARP request 后的 ARP reply报文。

reply 报文的 ARP 报文部分,就是已经确定的 MAC 与 IP 地址了;而 ARP 的攻击的方式,一般都是从这里入手。毕竟一个广播帧任何设备都可以收到,在正常情况下,只有对应的才会回复;倘若是个 ARP 攻击设备,不管收到啥,都回复 reply 报文,并改为自己的 MAC 地址,其他设备上的 ARP 缓存表不一会儿就乱了。4.5 在 Ubuntu 上查看 ARP 缓存表的信息

在 root 的权限下,可以使用 arp -d xxxx 命令删除指定的表项,搭配 ping 与 wireshark 可以看到一个设备在没有 ARP 缓存表项时设备的策略。没有对应的表项,就先发送 ARP 报文以获取对应的 IP 与 MAC 关系,然后再发送 ping 命令。
如果有对应的表项,就直接发送 ping 命令,wireshark 就不能抓到 arp 的报文了。
Attention:我这里能看到 10 与 12 的原因是,我们这边的子网掩码是 16 位,也就是说,是属于同一个网段的,并不是分属 10 与 12 网段。一般不是本网段的 IP 包在数据发送时,直接把 ETH 的 dst 设置为网关地址了。
4.6 VLAN 功能
在学习交换机的功能时,vlan 是一个可以划分不同组的一项功能;一旦在交换机中设置了 vlan 功能,只有相同的 vlan 的设备才能直接通信。而 vlan 标识的功能实现,就是在 ETH 帧上附着了 VLAN 字段,通过该字段来划分对应的网络。 既然是实现在 ETH 帧上,ARP ,IP 等报文也是符合这个标准的。
4.7 lwip 的 ARP 缓存表策略探究
lwip 的 ARP 缓存表的更新,基本是放在 etharp_input 函数中,这也可以理解;毕竟收到 arp_reply 数据包后更新 ARP 缓存表就行了。
那我们如果在收到 arp_reply 的情况下,并不更新 ARP 缓存表,还会有数据发出吗?我们注释掉这个函数来试一下:
void etharp_input(struct pbuf *p, struct netif *netif)
{
···
/* ARP message directed to us?
-> add IP address in ARP cache; assume requester wants to talk to us,
can result in directly sending the queued packets for this host.
ARP message not directed to us?
-> update the source IP address in the cache, if present */
// etharp_update_arp_entry(netif, &sipaddr, &(hdr->shwaddr),
// for_us ? ETHARP_FLAG_TRY_HARD : ETHARP_FLAG_FIND_ONLY);
···
}
开发板上发送 ping 命令:
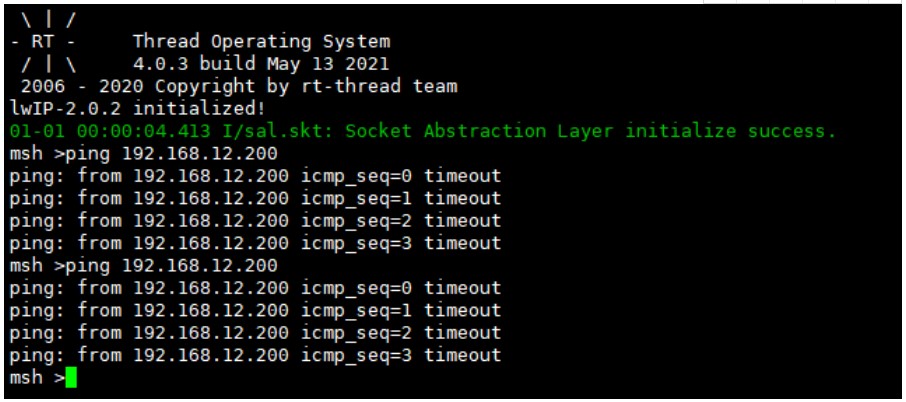
Ubuntu 上抓包:
由于开发板上屏蔽了 arp 缓存表的更新,即使收到了 ARP reply 也不会更新 ARP 表,则永远也不会有 PING 包从开发板发出,取而代之的是 ARP request 数据包。再上面代码的基础上,选择从 Ubuntu 上 PING 我们的开发板,在此之前先清空对应 ARP 的表项。
Ubuntu 删除表项并发送 ping 命令:

Ubuntu 上抓包:

可以看到 Ubuntu 发出了 ping 包,而发出的原因就是 Ubuntu 上已经由了 ARP 缓存,可以看到第 3174 帧就是 arp reply 。如果我们再注释掉,或者修改了 lwip 中的 arp reply 的代码,就可以实现比较初级的 ARP 攻击手段;怕挨打,就不做了,将来各位在实践时,哪怕是做出来也建议不要公开。
后面收到的 arp request 基本都是开发板发出的,因为开发板上没有对应的 ARP 表项,PING 的回复包一包也发不回来,导致Ubuntu 这边是 ping lost 状态。
原作者:xiangxistu












