三相交流电:
三相交流电是由三个频率相同、电势振幅相等、相位差互差120°角的交流电路组成的电力系统。日常用电系统中的三相四线制中电压为380/220V,即线电压为380V;相电压则随接线方式而异:若使用星形接法,相电压为220v;三角形接法,相电压则为380V。
三相电压:每根相线(火线)与中性线(零线)间的电压叫相电压,其有效值用UA、UB、UC表示;相线间的电压叫线电压,其有 效值用UAB、UBC、UCA表示。因为三相交流电源的三个线圈产生的交流电压相位相差120°,三个线圈作星形连接时,线电压等于相电压的根号3倍。我们通常讲的电压是220伏,380伏,就是三相四线制供电时的相电压和线电压。我国日常电路中,相电压是220V,线电压是380V(380V≈√3*220V)。工程上,讨论三相电源电压大小时,通常指的是电源的线电压。如三相四线制电源电压380V,指的是线电压380V。三相发电机在并网发电时或用三相电驱动三相交流电动机时,必须考虑相序的问题,否则会引起重大事故,为了防止接线错误,低压配电线路中规定用颜色区分各相,黄色表示A相,绿色表示B相,红色表示C相。
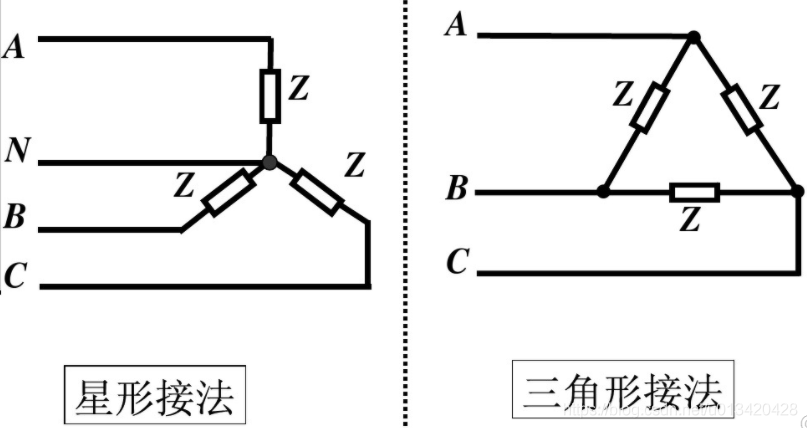
负载的两种接法(Y-型接法,Δ-型接法)
(电机正转-表达函数):
U a = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t ) U b = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t − 2 3 π ) U c = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t + 2 3 π ) begin{array}{l} Ua=Vm*cos(omega t) \ Ub=Vm*cos(omega t - frac{2}{3}pi) \ Uc=Vm*cos(omega t + frac{2}{3}pi) end{array} Ua=Vm∗cos(ωt)Ub=Vm∗cos(ωt−32π)Uc=Vm∗cos(ωt+32π)
(电机反转-表达函数):
U a = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t ) U b = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t + 2 3 π ) U c = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t − 2 3 π ) begin{array}{l} Ua=Vm*cos(omega t) \ Ub=Vm*cos(omega t + frac{2}{3}pi)\ Uc=Vm*cos(omega t - frac{2}{3}pi) end{array} Ua=Vm∗cos(ωt)Ub=Vm∗cos(ωt+32π)Uc=Vm∗cos(ωt−32π)
Vm:表示电压的幅度;
t:表示时间;
ω:角速度ω=Φ/t=2π/T=2πf,角速度等于2π除以周期,也等于2π乘以频率,其中:Φ角度, t时间, T周期, f频率, π圆周率;
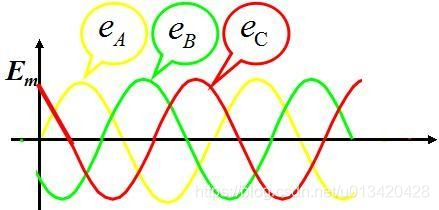
根据公式可以看出,三相电压是随时间变化的正弦波,相位差120°,如下图所示:
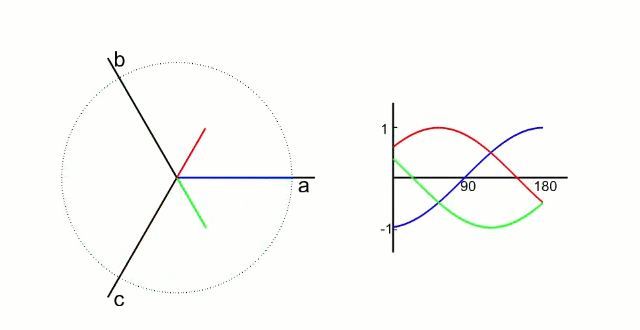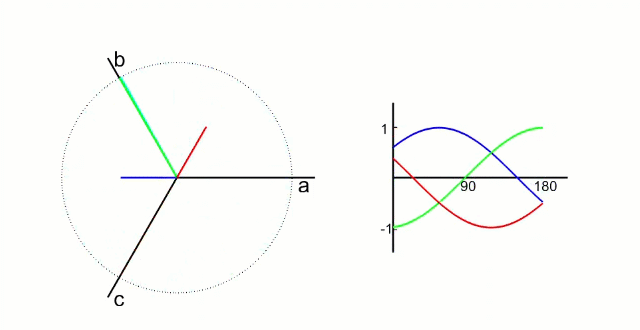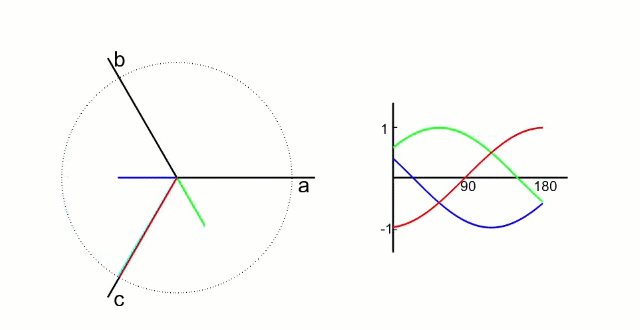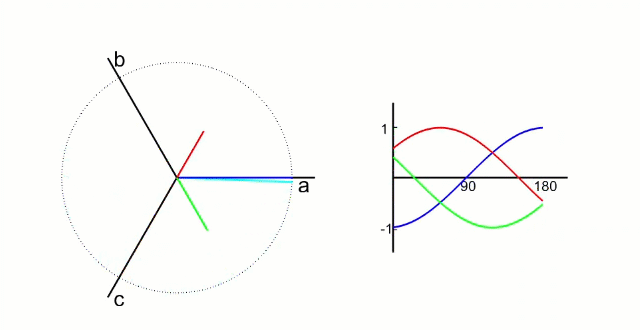
FOC控制中,有两种坐标转换,分别是clark变换和park变换:
clark变换将abc坐标系转换为αβ坐标系。
park变换将静止的αβ坐标系转换为旋转的dq坐标系。
逆变换:
iclark变换将αβ坐标系转换为abc坐标系。
ipark变换将旋转的dq坐标系转换为静止的αβ坐标系。
αβ坐标系:α轴β轴相位差90°,如下图所示:
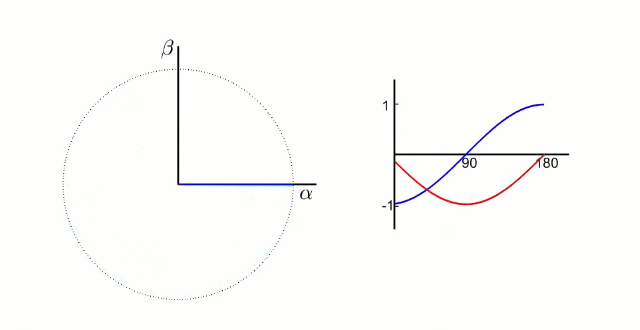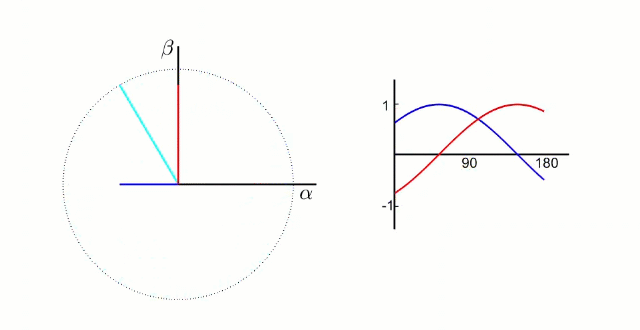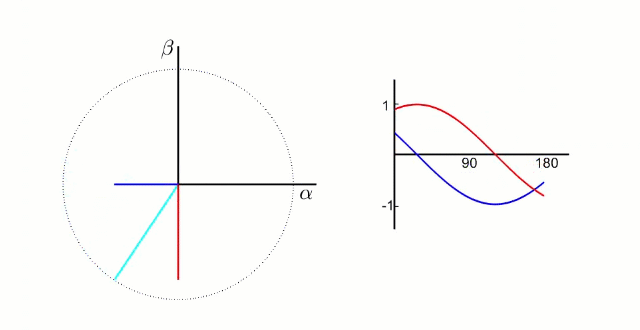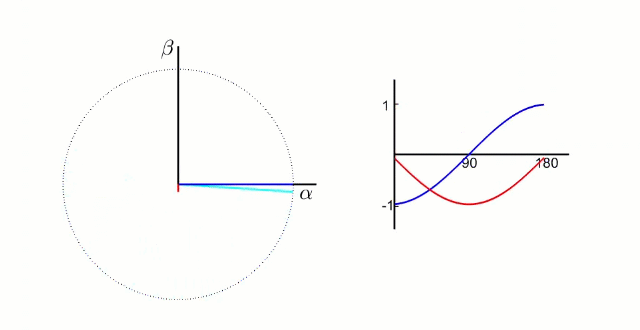
dq坐标系:dq坐标相对于定子是旋转坐标系,相对转子是静止坐标系(dq坐标旋转的角速度和转子的旋转角速度相同):
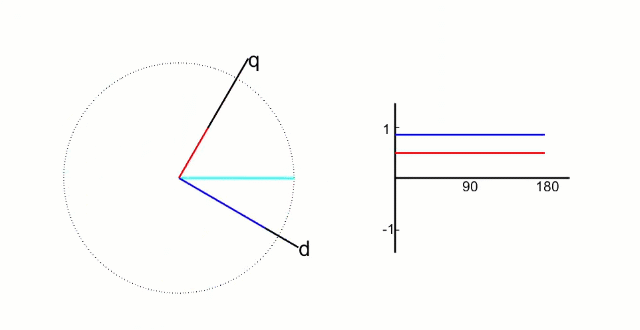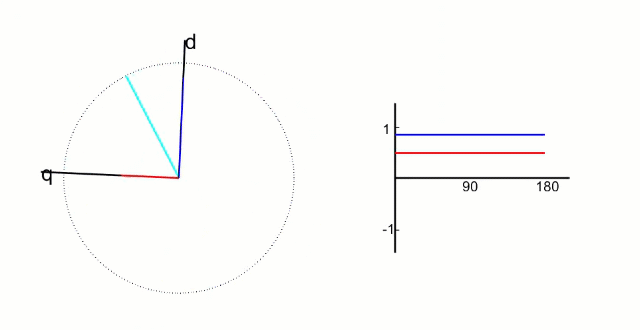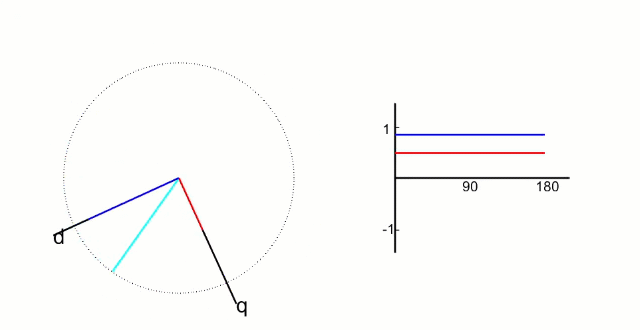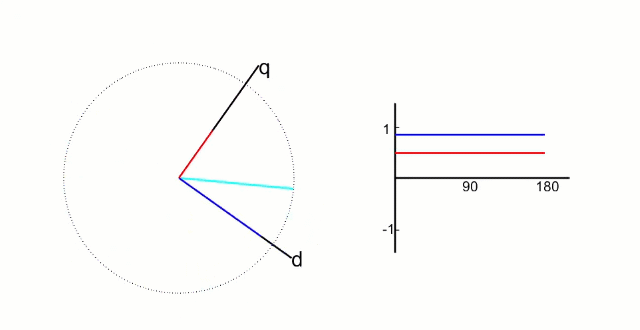
d轴方向与转子的磁链方向重和,又称为直轴;
q轴方向与转子的磁链方向垂直,又称为交轴;
电机功率P、转矩T、速度V 之间的关系:
功率=力·速度,表达公式:P=F·V
转矩(T)=扭力(F)·作用半径®, 推导出F=T/R
线速度(V)=2πR·每秒转速(n秒)
d轴:调节幅度(电机的转速);
q轴:调节相位(电机的转矩);
Clark Tranformation 3s-2s,clark转换公式:
[ U α U β ] = m ⋅ ∣ U a − U b ⋅ c o s ( 60 ° ) − U c ⋅ c o s ( 60 ° ) 0 U b ⋅ c o s ( 30 ° ) − U c ⋅ c o s ( 30 ° ) ∣ = m ⋅ [ 1 − 1 2 − 1 2 0 ( 3 ) 2 − ( 3 ) 2 ] ⋅ [ U a U b U c ] left[ begin{matrix} Ualpha \ Ubeta \ end{matrix} right] = m·left| begin{matrix} Ua&-Ub·cos(60°)&-Uc·cos(60°) \ 0 &Ub·cos(30°) &-Uc·cos(30°) end{matrix} right|= m· begin{bmatrix} 1& -frac{1}{2}&-frac{1}{2} \ 0 & frac{sqrt(3)}{2} &-frac{sqrt(3)}{2} end{bmatrix}⋅begin{bmatrix} Ua \ Ub \ Ucend{bmatrix} [UαUβ]=m⋅∣∣∣∣Ua0−Ub⋅cos(60°)Ub⋅cos(30°)−Uc⋅cos(60°)−Uc⋅cos(30°)∣∣∣∣=m⋅[10−212( 3)−21−2( 3)]⋅⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤
矩阵展开:
U α = m ⋅ ( U a − 1 2 ⋅ U b − 1 2 ⋅ U c ) U β = m ⋅ ( 3 2 ⋅ U b − 3 2 ⋅ U c ) begin{array}{l} Ualpha=m·(Ua-frac{1}{2}·Ub-frac{1}{2}·Uc) \ Ubeta=m·(frac{sqrt3}{2}·Ub-frac{sqrt3}{2}·Uc) end{array} Uα=m⋅(Ua−21⋅Ub−21⋅Uc)Uβ=m⋅(23 ⋅Ub−23 ⋅Uc)
若m=√(2/3),变换前后,功率不变。又称为:Concordia变换。
若m=2/3,变换前后,幅值不变,恒幅值。
将m=2/3代入式中得:
U α = U a U β = 1 3 ⋅ ( U a + 2 ⋅ U b ) begin{array}{l} Ualpha=Ua \ Ubeta=frac{1}{sqrt3}·(Ua+2·Ub) end{array} Uα=UaUβ=3 1⋅(Ua+2⋅Ub)
# Inverse Clark Transformation 2s-3s, iClark逆变换:
[ U a U b U c ] = m ′ ⋅ [ 1 0 − 1 2 3 2 − 1 2 − 3 2 ] ⋅ [ U α U β ] begin{bmatrix} Ua \ Ub \ Uc end{bmatrix} = m‘· begin{bmatrix} 1&0 \ -frac{1}{2} & frac{sqrt3}{2} \ -frac{1}{2}&-frac{sqrt3}{2} end{bmatrix}· begin{bmatrix} Ualpha \ Ubetaend{bmatrix} ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤=m′⋅⎣⎢⎡1−21−21023 −23 ⎦⎥⎤⋅[UαUβ]
矩阵展开:
U a = m ′ ⋅ ( U α ) U b = m ′ ⋅ ( − 1 2 ⋅ U α + 3 2 ⋅ U β ) U c = m ′ ⋅ ( − 1 2 ⋅ U α − 3 2 ⋅ U β ) begin{array}{l} Ua=m’·(Ualpha)\ Ub=m‘·(-frac{1}{2}·Ualpha+frac{sqrt3}{2}·Ubeta)\ Uc=m’·(-frac{1}{2}·Ualpha-frac{sqrt3}{2}·Ubeta) end{array} Ua=m′⋅(Uα)Ub=m′⋅(−21⋅Uα+23 ⋅Uβ)Uc=m′⋅(−21⋅Uα−23 ⋅Uβ)
若m′=√(2/3),变换前后,功率不变。
若m′=1,变换前后,幅值不变。
Park Transformation 3s-3r,park转换:
[ U d U q U 0 ] = 2 3 ⋅ [ c o s ( θ ) c o s ( θ − 2 3 π ) c o s ( θ + 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ ) − s i n ( θ − 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ + 2 3 π ) 1 2 1 2 1 2 ] ⋅ [ U a U b U c ] begin{bmatrix} Ud \ Uq \U0end{bmatrix} = frac{2}{3}·begin{bmatrix} cos(theta)&cos({theta-frac{2}{3}pi}) &cos(theta+frac{2}{3}pi) \ -sin(theta) & -sin(theta-frac{2}{3}pi)&-sin(theta+frac{2}{3}pi)\ frac{1}{2}&frac{1}{2}&frac{1}{2} end{bmatrix}· begin{bmatrix} Ua\Ub\Uc end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡UdUqU0⎦⎤=32⋅⎣⎡cos(θ)−sin(θ)21cos(θ−32π)−sin(θ−32π)21cos(θ+32π)−sin(θ+32π)21⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤
U d = U α ⋅ c o s ( θ ) + U β ⋅ s i n ( θ ) U q = U β ⋅ c o s ( θ ) − U α ⋅ s i n ( θ ) o r U d = U α ⋅ c o s ( θ ) + U β ⋅ s i n ( θ ) U q = − U α ⋅ s i n ( θ ) + U β ⋅ c o s ( θ ) Ud=Ualpha·cos(theta)+Ubeta·sin(theta) \ Uq=Ubeta·cos(theta)-Ualpha·sin(theta) \ or \ Ud=Ualpha·cos(theta)+Ubeta·sin(theta) \ Uq=-Ualpha·sin(theta)+Ubeta·cos(theta) Ud=Uα⋅cos(θ)+Uβ⋅sin(θ)Uq=Uβ⋅cos(θ)−Uα⋅sin(θ)orUd=Uα⋅cos(θ)+Uβ⋅sin(θ)Uq=−Uα⋅sin(θ)+Uβ⋅cos(θ)
inverse Park Tranformation 3r-3s,iPark逆转换:
[ U a U b U c ] = [ c o s ( θ ) − s i n ( θ ) 1 c o s ( θ − 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ − 2 3 π ) 1 c o s ( θ + 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ + 2 3 π ) 1 ] ⋅ [ U d U q U 0 ] begin{bmatrix}Ua\Ub\Ucend{bmatrix}= begin{bmatrix} cos(theta)&-sin(theta)&1 \ cos(theta - frac{2}{3}pi) & -sin(theta - frac{2}{3}pi) & 1 \ cos(theta + frac{2}{3}pi) & -sin(theta+frac{2}{3}pi) &1 end{bmatrix}⋅begin{bmatrix} Ud\Uq\U0 end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤=⎣⎡cos(θ)cos(θ−32π)cos(θ+32π)−sin(θ)−sin(θ−32π)−sin(θ+32π)111⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡UdUqU0⎦⎤
[ U α U β ] = [ c o s ( θ ) − s i n ( θ ) s i n ( θ ) c o s ( θ ) ] ⋅ [ U d U q ] begin{bmatrix} Ualpha \ Ubeta end{bmatrix} = begin{bmatrix} cos(theta)&-sin(theta) \ sin(theta)&cos(theta) end{bmatrix}· begin{bmatrix} Ud \ Uq end{bmatrix} [UαUβ]=[cos(θ)sin(θ)−sin(θ)cos(θ)]⋅[UdUq]
相关变量值:
π=180°(平角), 2π=360°(周角),这里π表示弧度
cos(60°) = 1/2 = 0.5
cos(30°) = √3/2 ≈ 0.866025
√3 = 1.7320508075688772935274463415059
2/3 = 0.66666666666666666666666666666667
√(2/3) = 0.81649658092772603273242802490196
Python matplotlib仿真代码:
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.pylab as plb
# 三相交流波形
Vm = 220 #电压幅度V
fHz=50 #频率
T=1/fHz #周期
Tn = 5 #显示n个周期的波形
t = np.linspace(0, T*Tn, 360*Tn) #时间t
theta = (2*np.pi*fHz) * t #电相角θ=2πf,随时间变化θ=ωt=2πf·t
Ua = Vm * np.cos((2*np.pi*fHz) * t) #U
Ub = Vm * np.cos((2*np.pi*fHz) * t - 2.0943)#(2/3)*np.pi) #V
Uc = Vm * np.cos((2*np.pi*fHz) * t + 2.0943)#(2/3)*np.pi) #W
#
Uo = (Ua+Ub+Uc) # (Ua+Ub+Uc)=0
plt.subplot(2,3,1)
plt.title(‘3-phase wave’)
plt.title(‘Set Paramter(3-phase wave Ua/Ub/Uc)’)
plt.plot(t, Ua, label=‘Ua’)
plt.plot(t, Ub, label=‘Ub’)
plt.plot(t, Uc, label=‘Uc’)
plt.plot(t, Uo, ‘b-。’,label=‘U0’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
# clark转换波形:
m = 2/3 #恒幅值
#m = np.sqrt(2/3) #恒功率
Ualpha = m * (Ua - (1/2)*Ub - (1/2)*Uc) #Uα
Ubeta = m * (np.sqrt(3)/2 * Ub - np.sqrt(3)/2*Uc) #Uβ
#Ualpha = Ua
#Ubeta = (1/np.sqrt(3))*(Ua + 2*Ub)
plt.subplot(2,3,2)
plt.title(‘Clark Tranformation(Ua/Ub/Uc to Uα/Uβ)’)
plt.plot(t, Ualpha, label=‘Uα’)
plt.plot(t, Ubeta, label=‘Uβ’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
# park转换波形:
Ud = Ualpha*np.cos(theta) + Ubeta*np.sin(theta)
Uq = -Ualpha*np.sin(theta) + Ubeta*np.cos(theta)
plt.subplot(2,3,3)
plt.title(‘Park Tranformation(Uα/Uβ to Uq/Ud)’)
plt.plot(t, Ud, ‘r’, label=‘Ud’)
plt.plot(t, Uq, ‘g’, label=‘Uq’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
# iPark
Udi = Ud-0 #调节幅度(电机的转速)
Uqi = Uq-0 #调节相位(电机的转矩)
#
plt.subplot(2,3,4)
plt.title(‘Set Paramter(Uq/Ud)’)
plt.plot(t, Udi, ‘r’, label=‘iUd’)
plt.plot(t, Uqi, ‘g’, label=‘iUq’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
Ualphai = Udi *np.cos(theta) - Uqi * np.sin(theta)
Ubetai = Udi * np.sin(theta) + Uqi * np.cos(theta)
plt.subplot(2,3,5)
plt.title(‘iPark Tranformation(Uq/Ud to Uα/Uβ)’)
plt.plot(t, Ualphai, label=‘iUα’)
plt.plot(t, Ubetai, label=‘iUβ’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
# iClark波形:
m = 1 #恒幅值
#m=np.sqrt(2/3) #恒功率
Uai = m * (Ualphai +(0*Ubetai))
Ubi = m * (-(1/2)*Ualphai + (np.sqrt(3)/2)*Ubetai)
Uci = m * (-(1/2)*Ualphai - (np.sqrt(3)/2)*Ubetai)
plt.subplot(2,3,6)
plt.title(‘iClark Tranformation(Uα/Uβ to Ua/Ub/Uc)’)
plt.plot(t, Uai, label=‘iUa’)
plt.plot(t, Ubi, label=‘iUb’)
plt.plot(t, Uci, label=‘iUc’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
# 显示图像
plt.show()
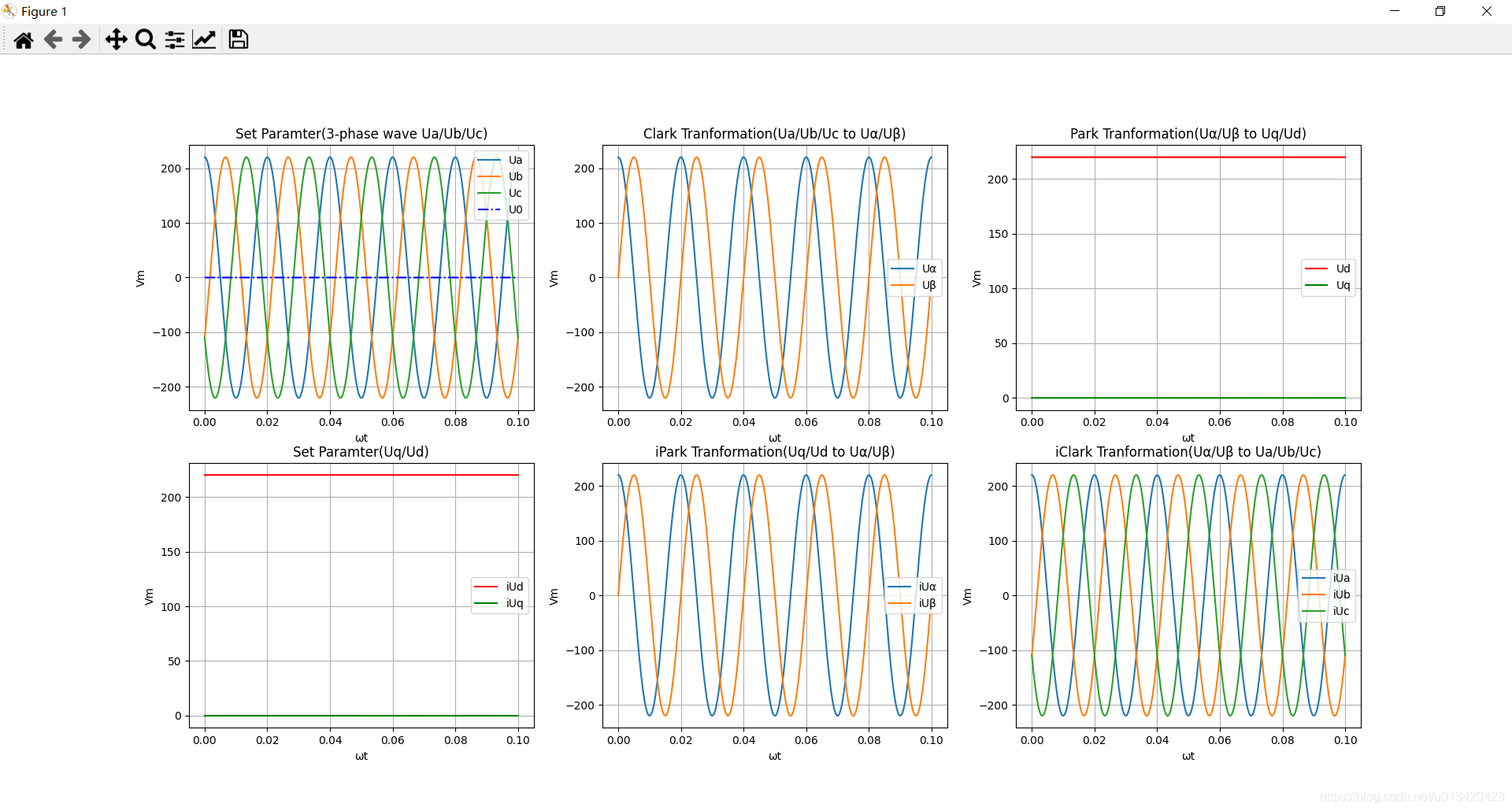
仿真波形:
三相交流电:
三相交流电是由三个频率相同、电势振幅相等、相位差互差120°角的交流电路组成的电力系统。日常用电系统中的三相四线制中电压为380/220V,即线电压为380V;相电压则随接线方式而异:若使用星形接法,相电压为220v;三角形接法,相电压则为380V。
三相电压:每根相线(火线)与中性线(零线)间的电压叫相电压,其有效值用UA、UB、UC表示;相线间的电压叫线电压,其有 效值用UAB、UBC、UCA表示。因为三相交流电源的三个线圈产生的交流电压相位相差120°,三个线圈作星形连接时,线电压等于相电压的根号3倍。我们通常讲的电压是220伏,380伏,就是三相四线制供电时的相电压和线电压。我国日常电路中,相电压是220V,线电压是380V(380V≈√3*220V)。工程上,讨论三相电源电压大小时,通常指的是电源的线电压。如三相四线制电源电压380V,指的是线电压380V。三相发电机在并网发电时或用三相电驱动三相交流电动机时,必须考虑相序的问题,否则会引起重大事故,为了防止接线错误,低压配电线路中规定用颜色区分各相,黄色表示A相,绿色表示B相,红色表示C相。

负载的两种接法(Y-型接法,Δ-型接法)

(电机正转-表达函数):
U a = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t ) U b = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t − 2 3 π ) U c = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t + 2 3 π ) begin{array}{l} Ua=Vm*cos(omega t) \ Ub=Vm*cos(omega t - frac{2}{3}pi) \ Uc=Vm*cos(omega t + frac{2}{3}pi) end{array} Ua=Vm∗cos(ωt)Ub=Vm∗cos(ωt−32π)Uc=Vm∗cos(ωt+32π)
(电机反转-表达函数):
U a = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t ) U b = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t + 2 3 π ) U c = V m ∗ c o s ( ω t − 2 3 π ) begin{array}{l} Ua=Vm*cos(omega t) \ Ub=Vm*cos(omega t + frac{2}{3}pi)\ Uc=Vm*cos(omega t - frac{2}{3}pi) end{array} Ua=Vm∗cos(ωt)Ub=Vm∗cos(ωt+32π)Uc=Vm∗cos(ωt−32π)
Vm:表示电压的幅度;
t:表示时间;
ω:角速度ω=Φ/t=2π/T=2πf,角速度等于2π除以周期,也等于2π乘以频率,其中:Φ角度, t时间, T周期, f频率, π圆周率;
根据公式可以看出,三相电压是随时间变化的正弦波,相位差120°,如下图所示:
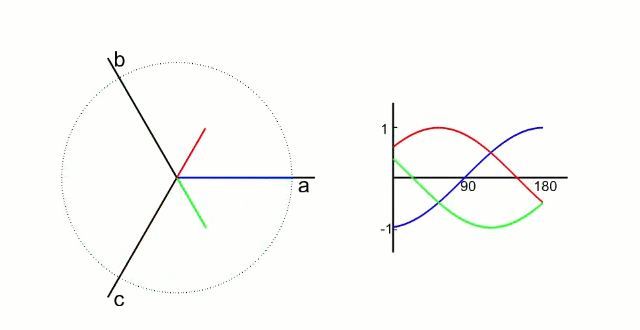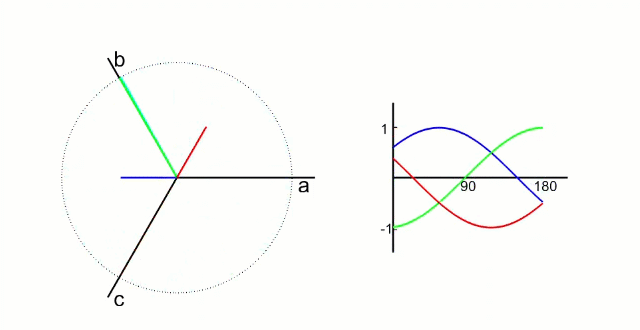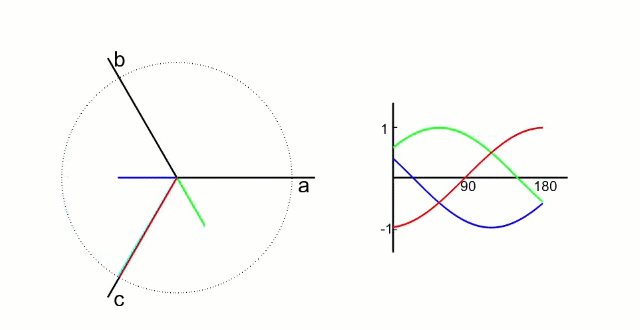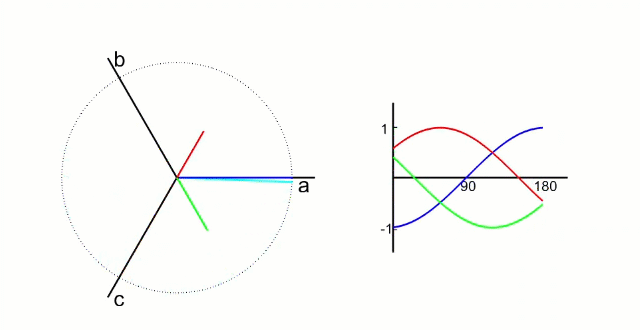
FOC控制中,有两种坐标转换,分别是clark变换和park变换:
clark变换将abc坐标系转换为αβ坐标系。
park变换将静止的αβ坐标系转换为旋转的dq坐标系。
逆变换:
iclark变换将αβ坐标系转换为abc坐标系。
ipark变换将旋转的dq坐标系转换为静止的αβ坐标系。
αβ坐标系:α轴β轴相位差90°,如下图所示:
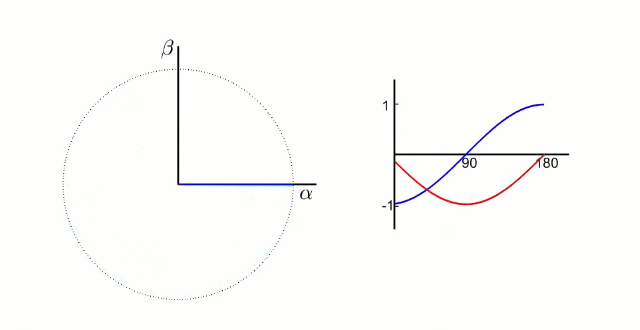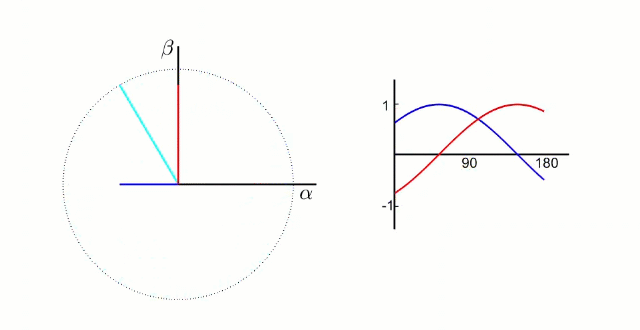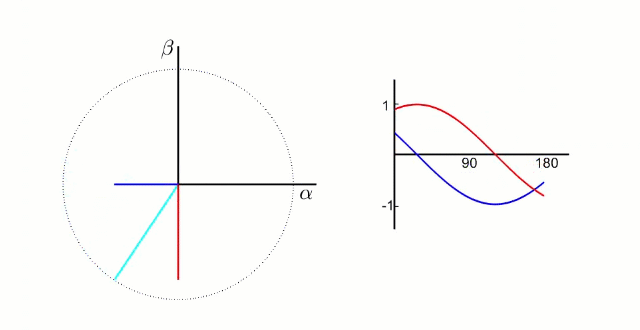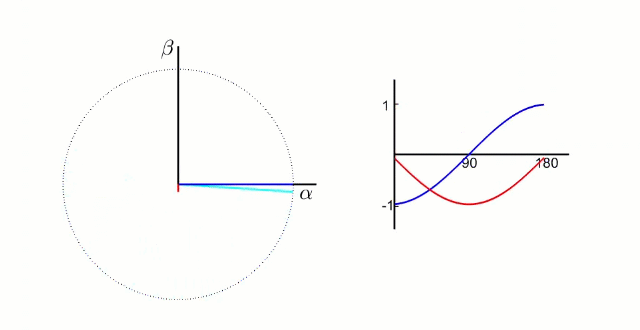
dq坐标系:dq坐标相对于定子是旋转坐标系,相对转子是静止坐标系(dq坐标旋转的角速度和转子的旋转角速度相同):

d轴方向与转子的磁链方向重和,又称为直轴;
q轴方向与转子的磁链方向垂直,又称为交轴;
电机功率P、转矩T、速度V 之间的关系:
功率=力·速度,表达公式:P=F·V
转矩(T)=扭力(F)·作用半径®, 推导出F=T/R
线速度(V)=2πR·每秒转速(n秒)
d轴:调节幅度(电机的转速);
q轴:调节相位(电机的转矩);
Clark Tranformation 3s-2s,clark转换公式:
[ U α U β ] = m ⋅ ∣ U a − U b ⋅ c o s ( 60 ° ) − U c ⋅ c o s ( 60 ° ) 0 U b ⋅ c o s ( 30 ° ) − U c ⋅ c o s ( 30 ° ) ∣ = m ⋅ [ 1 − 1 2 − 1 2 0 ( 3 ) 2 − ( 3 ) 2 ] ⋅ [ U a U b U c ] left[ begin{matrix} Ualpha \ Ubeta \ end{matrix} right] = m·left| begin{matrix} Ua&-Ub·cos(60°)&-Uc·cos(60°) \ 0 &Ub·cos(30°) &-Uc·cos(30°) end{matrix} right|= m· begin{bmatrix} 1& -frac{1}{2}&-frac{1}{2} \ 0 & frac{sqrt(3)}{2} &-frac{sqrt(3)}{2} end{bmatrix}⋅begin{bmatrix} Ua \ Ub \ Ucend{bmatrix} [UαUβ]=m⋅∣∣∣∣Ua0−Ub⋅cos(60°)Ub⋅cos(30°)−Uc⋅cos(60°)−Uc⋅cos(30°)∣∣∣∣=m⋅[10−212( 3)−21−2( 3)]⋅⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤
矩阵展开:
U α = m ⋅ ( U a − 1 2 ⋅ U b − 1 2 ⋅ U c ) U β = m ⋅ ( 3 2 ⋅ U b − 3 2 ⋅ U c ) begin{array}{l} Ualpha=m·(Ua-frac{1}{2}·Ub-frac{1}{2}·Uc) \ Ubeta=m·(frac{sqrt3}{2}·Ub-frac{sqrt3}{2}·Uc) end{array} Uα=m⋅(Ua−21⋅Ub−21⋅Uc)Uβ=m⋅(23 ⋅Ub−23 ⋅Uc)
若m=√(2/3),变换前后,功率不变。又称为:Concordia变换。
若m=2/3,变换前后,幅值不变,恒幅值。
将m=2/3代入式中得:
U α = U a U β = 1 3 ⋅ ( U a + 2 ⋅ U b ) begin{array}{l} Ualpha=Ua \ Ubeta=frac{1}{sqrt3}·(Ua+2·Ub) end{array} Uα=UaUβ=3 1⋅(Ua+2⋅Ub)
# Inverse Clark Transformation 2s-3s, iClark逆变换:
[ U a U b U c ] = m ′ ⋅ [ 1 0 − 1 2 3 2 − 1 2 − 3 2 ] ⋅ [ U α U β ] begin{bmatrix} Ua \ Ub \ Uc end{bmatrix} = m‘· begin{bmatrix} 1&0 \ -frac{1}{2} & frac{sqrt3}{2} \ -frac{1}{2}&-frac{sqrt3}{2} end{bmatrix}· begin{bmatrix} Ualpha \ Ubetaend{bmatrix} ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤=m′⋅⎣⎢⎡1−21−21023 −23 ⎦⎥⎤⋅[UαUβ]
矩阵展开:
U a = m ′ ⋅ ( U α ) U b = m ′ ⋅ ( − 1 2 ⋅ U α + 3 2 ⋅ U β ) U c = m ′ ⋅ ( − 1 2 ⋅ U α − 3 2 ⋅ U β ) begin{array}{l} Ua=m’·(Ualpha)\ Ub=m‘·(-frac{1}{2}·Ualpha+frac{sqrt3}{2}·Ubeta)\ Uc=m’·(-frac{1}{2}·Ualpha-frac{sqrt3}{2}·Ubeta) end{array} Ua=m′⋅(Uα)Ub=m′⋅(−21⋅Uα+23 ⋅Uβ)Uc=m′⋅(−21⋅Uα−23 ⋅Uβ)
若m′=√(2/3),变换前后,功率不变。
若m′=1,变换前后,幅值不变。
Park Transformation 3s-3r,park转换:
[ U d U q U 0 ] = 2 3 ⋅ [ c o s ( θ ) c o s ( θ − 2 3 π ) c o s ( θ + 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ ) − s i n ( θ − 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ + 2 3 π ) 1 2 1 2 1 2 ] ⋅ [ U a U b U c ] begin{bmatrix} Ud \ Uq \U0end{bmatrix} = frac{2}{3}·begin{bmatrix} cos(theta)&cos({theta-frac{2}{3}pi}) &cos(theta+frac{2}{3}pi) \ -sin(theta) & -sin(theta-frac{2}{3}pi)&-sin(theta+frac{2}{3}pi)\ frac{1}{2}&frac{1}{2}&frac{1}{2} end{bmatrix}· begin{bmatrix} Ua\Ub\Uc end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡UdUqU0⎦⎤=32⋅⎣⎡cos(θ)−sin(θ)21cos(θ−32π)−sin(θ−32π)21cos(θ+32π)−sin(θ+32π)21⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤
U d = U α ⋅ c o s ( θ ) + U β ⋅ s i n ( θ ) U q = U β ⋅ c o s ( θ ) − U α ⋅ s i n ( θ ) o r U d = U α ⋅ c o s ( θ ) + U β ⋅ s i n ( θ ) U q = − U α ⋅ s i n ( θ ) + U β ⋅ c o s ( θ ) Ud=Ualpha·cos(theta)+Ubeta·sin(theta) \ Uq=Ubeta·cos(theta)-Ualpha·sin(theta) \ or \ Ud=Ualpha·cos(theta)+Ubeta·sin(theta) \ Uq=-Ualpha·sin(theta)+Ubeta·cos(theta) Ud=Uα⋅cos(θ)+Uβ⋅sin(θ)Uq=Uβ⋅cos(θ)−Uα⋅sin(θ)orUd=Uα⋅cos(θ)+Uβ⋅sin(θ)Uq=−Uα⋅sin(θ)+Uβ⋅cos(θ)
inverse Park Tranformation 3r-3s,iPark逆转换:
[ U a U b U c ] = [ c o s ( θ ) − s i n ( θ ) 1 c o s ( θ − 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ − 2 3 π ) 1 c o s ( θ + 2 3 π ) − s i n ( θ + 2 3 π ) 1 ] ⋅ [ U d U q U 0 ] begin{bmatrix}Ua\Ub\Ucend{bmatrix}= begin{bmatrix} cos(theta)&-sin(theta)&1 \ cos(theta - frac{2}{3}pi) & -sin(theta - frac{2}{3}pi) & 1 \ cos(theta + frac{2}{3}pi) & -sin(theta+frac{2}{3}pi) &1 end{bmatrix}⋅begin{bmatrix} Ud\Uq\U0 end{bmatrix} ⎣⎡UaUbUc⎦⎤=⎣⎡cos(θ)cos(θ−32π)cos(θ+32π)−sin(θ)−sin(θ−32π)−sin(θ+32π)111⎦⎤⋅⎣⎡UdUqU0⎦⎤
[ U α U β ] = [ c o s ( θ ) − s i n ( θ ) s i n ( θ ) c o s ( θ ) ] ⋅ [ U d U q ] begin{bmatrix} Ualpha \ Ubeta end{bmatrix} = begin{bmatrix} cos(theta)&-sin(theta) \ sin(theta)&cos(theta) end{bmatrix}· begin{bmatrix} Ud \ Uq end{bmatrix} [UαUβ]=[cos(θ)sin(θ)−sin(θ)cos(θ)]⋅[UdUq]
相关变量值:
π=180°(平角), 2π=360°(周角),这里π表示弧度
cos(60°) = 1/2 = 0.5
cos(30°) = √3/2 ≈ 0.866025
√3 = 1.7320508075688772935274463415059
2/3 = 0.66666666666666666666666666666667
√(2/3) = 0.81649658092772603273242802490196
Python matplotlib仿真代码:
import numpy as np
import scipy as sp
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.pylab as plb
# 三相交流波形
Vm = 220 #电压幅度V
fHz=50 #频率
T=1/fHz #周期
Tn = 5 #显示n个周期的波形
t = np.linspace(0, T*Tn, 360*Tn) #时间t
theta = (2*np.pi*fHz) * t #电相角θ=2πf,随时间变化θ=ωt=2πf·t
Ua = Vm * np.cos((2*np.pi*fHz) * t) #U
Ub = Vm * np.cos((2*np.pi*fHz) * t - 2.0943)#(2/3)*np.pi) #V
Uc = Vm * np.cos((2*np.pi*fHz) * t + 2.0943)#(2/3)*np.pi) #W
#
Uo = (Ua+Ub+Uc) # (Ua+Ub+Uc)=0
plt.subplot(2,3,1)
plt.title(‘3-phase wave’)
plt.title(‘Set Paramter(3-phase wave Ua/Ub/Uc)’)
plt.plot(t, Ua, label=‘Ua’)
plt.plot(t, Ub, label=‘Ub’)
plt.plot(t, Uc, label=‘Uc’)
plt.plot(t, Uo, ‘b-。’,label=‘U0’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
# clark转换波形:
m = 2/3 #恒幅值
#m = np.sqrt(2/3) #恒功率
Ualpha = m * (Ua - (1/2)*Ub - (1/2)*Uc) #Uα
Ubeta = m * (np.sqrt(3)/2 * Ub - np.sqrt(3)/2*Uc) #Uβ
#Ualpha = Ua
#Ubeta = (1/np.sqrt(3))*(Ua + 2*Ub)
plt.subplot(2,3,2)
plt.title(‘Clark Tranformation(Ua/Ub/Uc to Uα/Uβ)’)
plt.plot(t, Ualpha, label=‘Uα’)
plt.plot(t, Ubeta, label=‘Uβ’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.grid()
plt.legend()
# park转换波形:
Ud = Ualpha*np.cos(theta) + Ubeta*np.sin(theta)
Uq = -Ualpha*np.sin(theta) + Ubeta*np.cos(theta)
plt.subplot(2,3,3)
plt.title(‘Park Tranformation(Uα/Uβ to Uq/Ud)’)
plt.plot(t, Ud, ‘r’, label=‘Ud’)
plt.plot(t, Uq, ‘g’, label=‘Uq’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
# iPark
Udi = Ud-0 #调节幅度(电机的转速)
Uqi = Uq-0 #调节相位(电机的转矩)
#
plt.subplot(2,3,4)
plt.title(‘Set Paramter(Uq/Ud)’)
plt.plot(t, Udi, ‘r’, label=‘iUd’)
plt.plot(t, Uqi, ‘g’, label=‘iUq’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
Ualphai = Udi *np.cos(theta) - Uqi * np.sin(theta)
Ubetai = Udi * np.sin(theta) + Uqi * np.cos(theta)
plt.subplot(2,3,5)
plt.title(‘iPark Tranformation(Uq/Ud to Uα/Uβ)’)
plt.plot(t, Ualphai, label=‘iUα’)
plt.plot(t, Ubetai, label=‘iUβ’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
# iClark波形:
m = 1 #恒幅值
#m=np.sqrt(2/3) #恒功率
Uai = m * (Ualphai +(0*Ubetai))
Ubi = m * (-(1/2)*Ualphai + (np.sqrt(3)/2)*Ubetai)
Uci = m * (-(1/2)*Ualphai - (np.sqrt(3)/2)*Ubetai)
plt.subplot(2,3,6)
plt.title(‘iClark Tranformation(Uα/Uβ to Ua/Ub/Uc)’)
plt.plot(t, Uai, label=‘iUa’)
plt.plot(t, Ubi, label=‘iUb’)
plt.plot(t, Uci, label=‘iUc’)
plt.xlabel(‘ωt’)
plt.ylabel(‘Vm’)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
# 显示图像
plt.show()
仿真波形:


 举报
举报



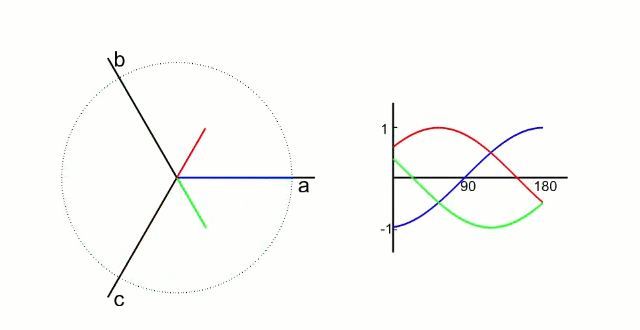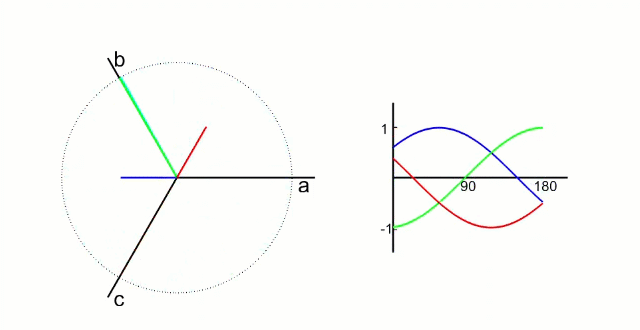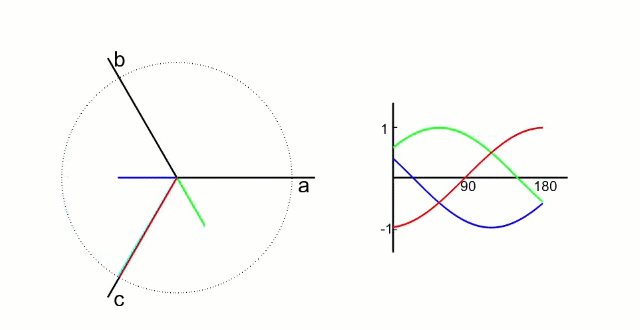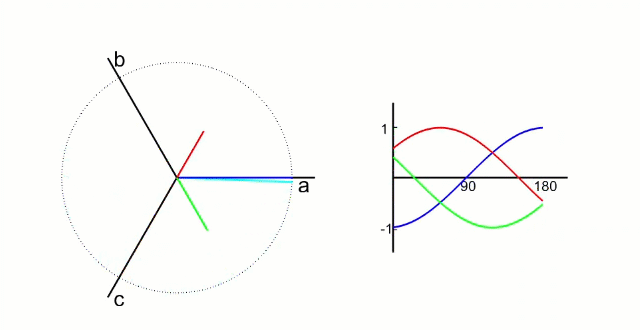
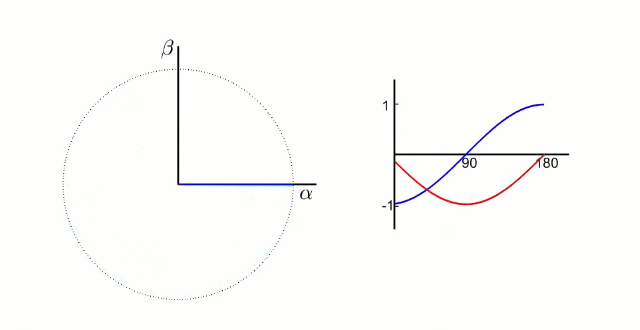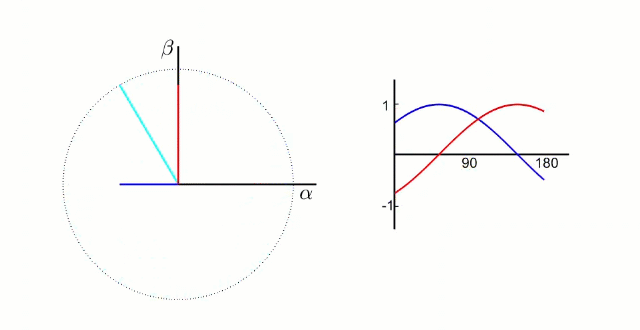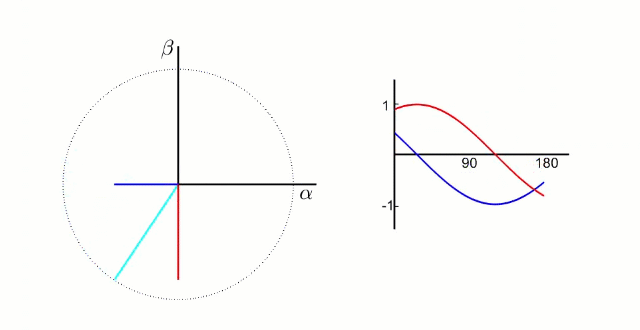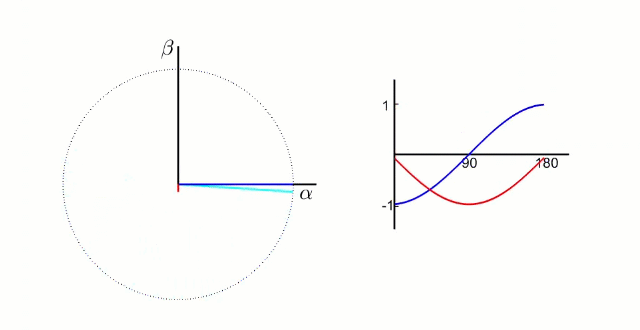



 举报
举报

