[文章]OpenHarmony:如何使用HDF平台驱动控制I2C
1
1
1、程序介绍
本程序是基于OpenHarmony标准系统编写的平台驱动案例:I2C
目前已在凌蒙派-RK3568开发板跑通。详细资料请参考官网:https://gitee.com/Lockzhiner-Ele ... platform_device_i2c
详细资料请参考官网:
- I2C平台驱动开发
- I2C应用程序开发
2.1、I2C简介
I2C(Inter Integrated Circuit)总线是由Philips公司开发的一种简单、双向二线制同步串行总线。由于其硬件连接简单、成本低廉,因此被广泛应用于各种短距离通信的场景。
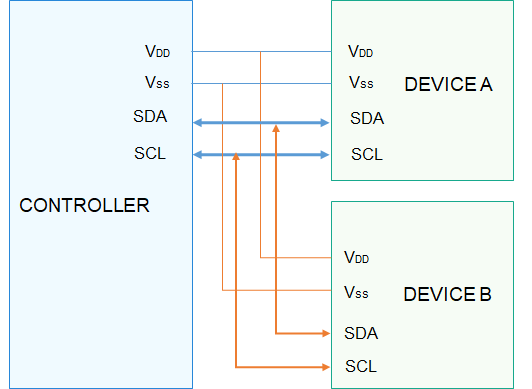
I2C以主从方式工作,通常有一个主设备和一个或者多个从设备,主从设备通过SDA(SerialData)串行数据线以及SCL(SerialClock)串行时钟线两根线相连(如图1)。
I2C数据的传输必须以一个起始信号作为开始条件,以一个结束信号作为传输的停止条件。数据传输以字节为单位,高位在前,逐个bit进行传输。
I2C总线上的每一个设备都可以作为主设备或者从设备,而且每一个设备都会对应一个唯一的地址,当主设备需要和某一个从设备通信时,通过广播的方式,将从设备地址写到总线上,如果某个从设备符合此地址,将会发出应答信号,建立传输。
I2C接口定义了完成I2C传输的通用方法集合,包括:
- I2C控制器管理:打开或关闭I2C控制器
- I2C消息传输:通过消息传输结构体数组进行自定义传输
I2C物理连线示意图
2.2、I2C驱动开发
2.2.1、I2C驱动开发接口
为了保证上层在调用I2C接口时能够正确的操作硬件,核心层在//drivers/hdf_core/framework/support/platform/include/i2c/i2c_core.h中定义了以下钩子函数。驱动适配者需要在适配层实现这些函数的具体功能,并与这些钩子函数挂接,从而完成接口层与核心层的交互。
I2cMethod和I2cLockMethod定义:
- struct I2cMethod {
- int32_t (*transfer)(struct I2cCntlr *cntlr, struct I2cMsg *msgs, int16_t count);
- };
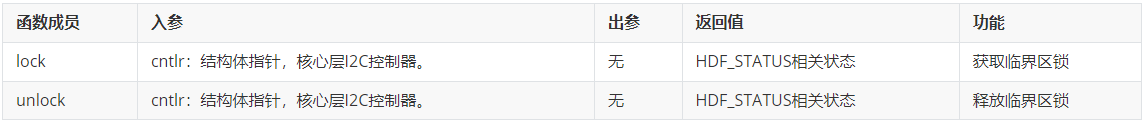
- struct I2cLockMethod { // 锁机制操作结构体
- int32_t (*lock)(struct I2cCntlr *cntlr);
- void (*unlock)(struct I2cCntlr *cntlr);
- };
- static int32_t I2cCntlrLockDefault(struct I2cCntlr *cntlr)
- {
- if (cntlr == NULL) {
- return HDF_ERR_INVALID_OBJECT;
- }
- return OsalMutexLock(&cntlr->lock);
- }
- static void I2cCntlrUnlockDefault(struct I2cCntlr *cntlr)
- {
- if (cntlr == NULL) {
- return;
- }
- (void)OsalMutexUnlock(&cntlr->lock);
- }
- static const struct I2cLockMethod g_i2cLockOpsDefault = {
- .lock = I2cCntlrLockDefault,
- .unlock = I2cCntlrUnlockDefault,
- };
I2cMethod结构体成员函数功能说明:
I2cLockMethod结构体成员函数功能说明:
2.2.2、I2C驱动开发步骤
I2C模块适配HDF框架包含以下四个步骤:
- 实例化驱动入口。
- 配置属性文件。
- 实例化I2C控制器对象。
- 驱动调试。
2.2.2.1、驱动实例化驱动入口
I2C控制器会出现很多个设备挂接的情况,因而在HDF框架中首先会为此类型的设备创建一个管理器对象,并同时对外发布一个管理器服务来统一处理外部访问。这样,用户需要打开某个设备时,会先获取到管理器服务,然后管理器服务根据用户指定参数查找到指定设备。
I2C管理器服务的驱动由核心层实现,驱动适配者不需要关注这部分内容的实现,但在实现Init函数的时候需要调用核心层的I2cCntlrAdd函数,它会实现相应功能。
I2C驱动入口开发参考:
- struct HdfDriverEntry g_i2cLinuxDriverEntry = {
- .moduleVersion = 1,
- .Bind = LinuxI2cBind,
- .Init = LinuxI2cInit,
- .Release = LinuxI2cRelease,
- .moduleName = "linux_i2c_adapter", // 【必要且与device_info.hcs文件里面匹配】
- };
- HDF_INIT(g_i2cLinuxDriverEntry); // 调用HDF_INIT将驱动入口注册到HDF框架中
- /* 核心层i2c_core.c管理器服务的驱动入口 */
- struct HdfDriverEntry g_i2cManagerEntry = {
- .moduleVersion = 1,
- .Bind = I2cManagerBind,
- .Init = I2cManagerInit,
- .Release = I2cManagerRelease,
- .moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_I2C_MANAGER", // 这与device_info.hcs文件中device0对应
- };
- HDF_INIT(g_i2cManagerEntry);
deviceNode信息与驱动入口注册相关,器件属性值对于驱动适配者的驱动实现以及核心层I2cCntlr相关成员的默认值或限制范围有密切关系。
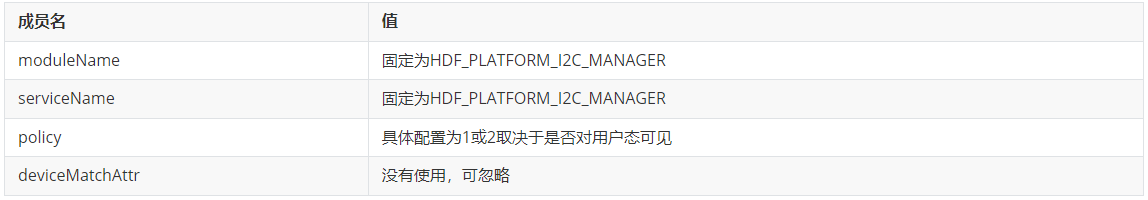
统一服务模式的特点是device_info.hcs文件中第一个设备节点必须为I2C管理器,其各项参数如下所示:
从第二个节点开始配置具体I2C控制器信息,此节点并不表示某一路I2C控制器,而是代表一个资源性质设备,用于描述一类I2C控制器的信息。多个控制器之间相互区分的参数是busId和reg_pbase,这在i2c_config.hcs文件中有所体现。
本次案例以rk3568为案例(即文件//vendor/lockzhiner/rk3568/hdf_config/khdf/device_info/device_info.hcs),添加deviceNode描述,具体修改如下:
- device_i2c :: device {
- device0 :: deviceNode {
- policy = 2;
- priority = 50;
- permission = 0644;
- moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_I2C_MANAGER";
- serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_I2C_MANAGER";
- deviceMatchAttr = "hdf_platform_i2c_manager";
- }
- device1 :: deviceNode {
- policy = 0; // 等于0,不需要发布服务
- priority = 55; // 驱动启动优先级
- permission = 0644; // 驱动创建设备节点权限
- moduleName = "linux_i2c_adapter"; // 用于指定驱动名称,需要与期望的驱动Entry中的moduleName一致,必须是linux_i2c_adapter
- deviceMatchAttr = "linux_i2c_adapter"; // 用于配置控制器私有数据,要与i2c_config.hcs中对应控制器保持一致
- }
- }
- root {
- platform {
- i2c_config {
- match_attr = "linux_i2c_adapter"; // 需要和device_info.hcs中的deviceMatchAttr值一致
- template i2c_controller {
- bus = 0; // i2c控制器序号
- }
- controller_0x120b0000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 0;
- }
- controller_0x120b1000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 1;
- }
- controller_0x120b2000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 2;
- }
- controller_0x120b3000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 3;
- }
- controller_0x120b4000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 4;
- }
- controller_0x120b5000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 5;
- }
- controller_0x120b6000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 6;
- }
- controller_0x120b7000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 7;
- }
- }
- }
- }
完成驱动入口注册之后,下一步就是以核心层I2cCntlr对象的初始化为核心,包括驱动适配者自定义结构体(传递参数和数据),实例化I2cCntlr成员I2cMethod(让用户可以通过接口来调用驱动底层函数),实现HdfDriverEntry成员函数(Bind,Init,Release)。
- static int32_t LinuxI2cTransfer(struct I2cCntlr *cntlr, struct I2cMsg *msgs, int16_t count);
- // 定义I2cMethod结构体变量g_method,实现i2c相应接口
- static struct I2cMethod g_method = {
- .transfer = LinuxI2cTransfer,
- };
- static int32_t LinuxI2cBind(struct HdfDeviceObject *device);
- static int32_t LinuxI2cInit(struct HdfDeviceObject *device);
- static void LinuxI2cRelease(struct HdfDeviceObject *device);
- struct HdfDriverEntry g_i2cLinuxDriverEntry = {
- .moduleVersion = 1,
- .Bind = LinuxI2cBind,
- .Init = LinuxI2cInit,
- .Release = LinuxI2cRelease,
- .moduleName = "linux_i2c_adapter",
- };
- HDF_INIT(g_i2cLinuxDriverEntry);
建议先在Linux下修改确认,再移植到OpenHarmony。
2.3、I2C应用开发
2.3.1、接口说明
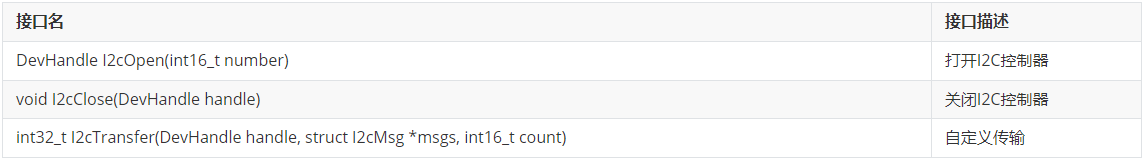
I2C模块提供的主要接口如表1所示,具体API详见//drivers/hdf_core/framework/include/platform/i2c_if.h。
I2C驱动API接口功能介绍如下所示:
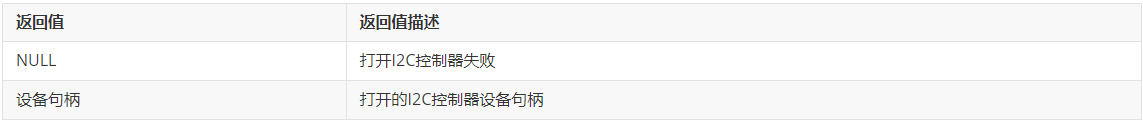
(1)I2cOpen
在进行I2C通信前,首先要调用I2cOpen打开I2C控制器。
- DevHandle I2cOpen(int16_t number);
I2cOpen返回值定义如下:
假设系统中存在8个I2C控制器,编号从0到7,以下代码示例为获取3号控制器:
- DevHandle i2cHandle = NULL; /* I2C控制器句柄 /
- /* 打开I2C控制器 */
- i2cHandle = I2cOpen(3);
- if (i2cHandle == NULL) {
- HDF_LOGE("I2cOpen: failed\n");
- return;
- }
I2C通信完成之后,需要关闭I2C控制器。
- void I2cClose(DevHandle handle);
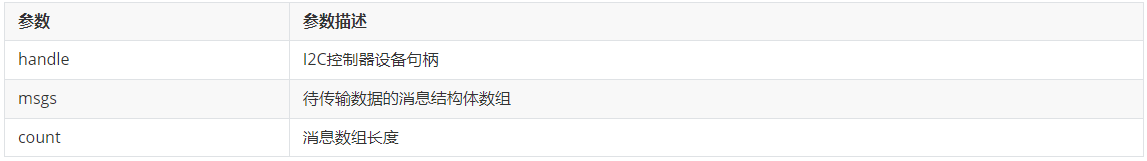
(3)I2cTransfer
i2c消息传输。
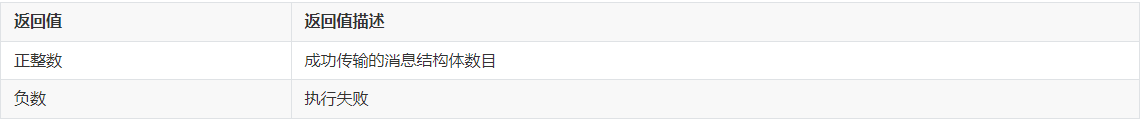
- int32_t I2cTransfer(DevHandle handle, struct I2cMsg \*msgs, int16_t count);
I2cTransfer返回值定义如下:
I2C传输消息类型为I2cMsg,每个传输消息结构体表示一次读或写,通过一个消息数组,可以执行若干次的读写组合操作。组合读写示例:
- int32_t ret;
- uint8_t wbuff[2] = { 0x12, 0x13 };
- uint8_t rbuff[2] = { 0 };
- struct I2cMsg msgs[2]; /* 自定义传输的消息结构体数组 */
- msgs[0].buf = wbuff; /* 写入的数据 */
- msgs[0].len = 2; /* 写入数据长度为2 */
- msgs[0].addr = 0x5A; /* 写入设备地址为0x5A */
- msgs[0].flags = 0; /* 传输标记为0,默认为写 */
- msgs[1].buf = rbuff; /* 要读取的数据 */
- msgs[1].len = 2; /* 读取数据长度为2 */
- msgs[1].addr = 0x5A; /* 读取设备地址为0x5A */
- msgs[1].flags = I2C_FLAG_READ /* I2C_FLAG_READ置位 */
- /* 进行一次自定义传输,传输的消息个数为2 */
- ret = I2cTransfer(i2cHandle, msgs, 2);
- if (ret != 2) {
- HDF_LOGE("I2cTransfer: failed, ret %d\n", ret);
- return;
- }
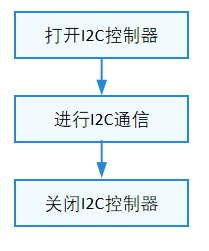
使用I2C设备的一般流程如下图所示:
3、程序解析
3.1、准备工作
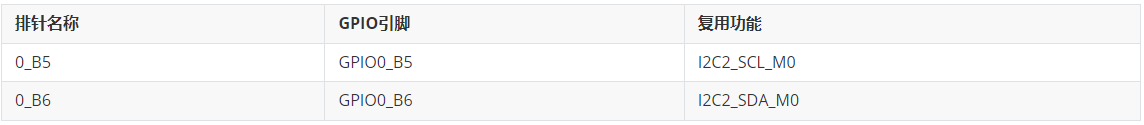
查看《凌蒙派-RK3568开发板_排针说明表_》(即Git仓库的//docs/board/凌蒙派-RK3568开发板_排针说明表_v1.0.xlsx),具体如下:
3.2、Linux内核解析
3.2.1、创建Linux内核Git
请参考《OpenHarmony如何为内核打patch》(即Git仓库的//docs/OpenHarmony如何为内核打patch.docx)。
3.2.2、修改设备树I2C2配置
修改//arch/arm64/boot/dts/rockchip/rk3568-lockzhiner.dtsi(即该目录是指已打Patch后的Linux内核,不是OpenHarmony主目录),定义i2c2启用,具体如下所示:
- &i2c2 {
- status = "okay";
- };
请参考《OpenHarmony如何为内核打patch》(即Git仓库的//docs/OpenHarmony如何为内核打patch.docx)。
3.2.4、替换OpenHarmony的内核patch
将制作出的kernel.patch替换到//kernel/linux/patches/linux-5.10/rk3568_patch/kernel.patch即可。
3.3、OpenHarmony配置树配置
3.3.1、device_info.hcs
//vendor/lockzhiner/rk3568/hdf_config/khdf/device_info/device_info.hcs已定义好,具体如下:
- device_i2c :: device {
- device0 :: deviceNode {
- policy = 2;
- priority = 50;
- permission = 0644;
- moduleName = "HDF_PLATFORM_I2C_MANAGER";
- serviceName = "HDF_PLATFORM_I2C_MANAGER";
- deviceMatchAttr = "hdf_platform_i2c_manager";
- }
- device1 :: deviceNode {
- policy = 0; // 等于0,不需要发布服务
- priority = 55;
- permission = 0644;
- moduleName = "linux_i2c_adapter";
- deviceMatchAttr = "linux_i2c_adapter";
- }
- }
- device1是rk3568原有的配置,也是我们需要的,作为OpenHarmony的i2c配置。
- moduleName定义为linux_i2c_adapter,表示该节点对应于//drivers/hdf_core/adapter/khdf/linux/platform/i2c/i2c_adapter.c,该驱动是对接Linux i2c子系统。
在//vendor/lockzhiner/rk3568/hdf_config/khdf/platform/i2c_config.hcs,具体内容如下:
- root {
- platform {
- i2c_config {
- match_attr = "linux_i2c_adapter";
- template i2c_controller {
- bus = 0;
- }
- controller_0x120b0000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 0;
- }
- controller_0x120b1000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 1;
- }
- controller_0x120b2000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 2;
- }
- controller_0x120b3000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 3;
- }
- controller_0x120b4000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 4;
- }
- controller_0x120b5000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 5;
- }
- controller_0x120b6000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 6;
- }
- controller_0x120b7000 :: i2c_controller {
- bus = 7;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- controller_0x120b2000是为i2c2准备的。
- bus用于定于Linux i2c控制器序号。
在//drivers/hdf_core/adapter/khdf/linux/platform/i2c/i2c_adapter.c已编写对接Linux I2C驱动的相关代码,具体内容如下:
- struct HdfDriverEntry g_i2cLinuxDriverEntry = {
- .moduleVersion = 1,
- .Bind = LinuxI2cBind,
- .Init = LinuxI2cInit,
- .Release = LinuxI2cRelease,
- .moduleName = "linux_i2c_adapter",
- };
- HDF_INIT(g_i2cLinuxDriverEntry);
3.5、应用程序3.5.1、i2c_test.c
i2c相关头文件如下所示:
- #include "i2c_if.h" // i2c标准接口头文件
其中,读操作源代码具体如下:
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- DevHandle handle = NULL;
- int32_t ret = 0;
- struct I2cMsg msgs[2]; // 消息结构体数组
- int16_t msgs_count = 0;
- uint8_t wbuff[STRING_MAXSIZE] = { 0 };
- uint8_t rbuff[STRING_MAXSIZE] = { 0 };
- // 解析参数
- ......
- // 打开i2c控制器
- handle = I2cOpen(m_i2c_number);
- if (handle == NULL) {
- PRINT_ERROR("I2cOpen failed\n");
- return -1;
- }
- if (m_i2c_flags_read == 1) {
- // 读操作
- // 设置msgs数组有效数目
- msgs_count = 2;
- // 初始化msgs[0],该部分为主设备发送从设备的i2c内容
- msgs[0].addr = m_i2c_slave_address;
- msgs[0].flags = toI2cFlags(0, m_i2c_flags_addr_10bit, m_i2c_flags_read_no_ack, m_i2c_flags_ignore_no_ack, m_i2c_flags_no_start, m_i2c_flags_stop);
- msgs[0].len = 1;
- wbuff[0] = m_i2c_reg_address; // 本案例的i2c从设备是第1字节是寄存器地址
- msgs[0].buf = wbuff;
- // 初始化msgs[1],该部分为主设备读取从设备发送的i2c内容
- msgs[1].addr = m_i2c_slave_address;
- msgs[1].flags = toI2cFlags(1, m_i2c_flags_addr_10bit, m_i2c_flags_read_no_ack, m_i2c_flags_ignore_no_ack, m_i2c_flags_no_start, m_i2c_flags_stop);
- msgs[1].len = m_i2c_read_data_length;
- msgs[1].buf = rbuff;
- // i2c数据传输,传输次数为2次
- ret = I2cTransfer(handle, msgs, msgs_count);
- if (ret != msgs_count) {
- PRINT_ERROR("I2cTransfer(read) failed and ret = %d\n", ret);
- goto out;
- }
- printf("I2cTransfer success and read data length = %d\n", strlen((char *)rbuff));
- for (uint32_t i = 0; i < strlen((char *)rbuff); i++) {
- printf("rbuff[%d] = 0x%x\n", i, rbuff[i]);
- }
- } else {
- ......
- }
- out:
- // 关闭i2c控制器
- I2cClose(handle);
- return ret;
- }
- int main(int argc, char* argv[])
- {
- DevHandle handle = NULL;
- int32_t ret = 0;
- struct I2cMsg msgs[2]; // 消息结构体数组
- int16_t msgs_count = 0;
- uint8_t wbuff[STRING_MAXSIZE] = { 0 };
- uint8_t rbuff[STRING_MAXSIZE] = { 0 };
- // 解析参数
- ......
- // 打开i2c控制器
- handle = I2cOpen(m_i2c_number);
- if (handle == NULL) {
- PRINT_ERROR("I2cOpen failed\n");
- return -1;
- }
- if (m_i2c_flags_read == 1) {
- ......
- } else {
- // 写操作
- // 设置msgs数组有效数目
- msgs_count = 1;
- // 初始化msgs[0],该部分为主设备发送从设备的i2c内容
- msgs[0].addr = m_i2c_slave_address;
- msgs[0].flags = toI2cFlags(0, m_i2c_flags_addr_10bit, m_i2c_flags_read_no_ack, m_i2c_flags_ignore_no_ack, m_i2c_flags_no_start, m_i2c_flags_stop);
- msgs[0].len = 2;
- wbuff[0] = m_i2c_reg_address; // 本案例的i2c从设备是第1字节是寄存器地址
- wbuff[1] = m_i2c_reg_value; // 本案例的i2c从设备是第2字节是寄存器数值
- msgs[0].buf = wbuff;
- // i2c数据传输,传输次数为2次
- ret = I2cTransfer(handle, msgs, msgs_count);
- if (ret != msgs_count) {
- PRINT_ERROR("I2cTransfer(write) failed and ret = %d\n", ret);
- goto out;
- }
- printf("I2cTransfer success and write reg(%d), data(%d)\n", m_i2c_reg_address, m_i2c_reg_value);
- }
- out:
- // 关闭i2c控制器
- I2cClose(handle);
- return ret;
- }
编写应用程序的BUILD.gn,具体内容如下:
- import("//build/ohos.gni")
- import("//drivers/hdf_core/adapter/uhdf2/uhdf.gni")
- print("samples: compile rk3568_i2c_test")
- ohos_executable("rk3568_i2c_test") {
- sources = [ "i2c_test.c" ]
- include_dirs = [
- "$hdf_framework_path/include",
- "$hdf_framework_path/include/core",
- "$hdf_framework_path/include/osal",
- "$hdf_framework_path/include/platform",
- "$hdf_framework_path/include/utils",
- "$hdf_uhdf_path/osal/include",
- "$hdf_uhdf_path/ipc/include",
- "//base/hiviewdfx/hilog/interfaces/native/kits/include",
- "//third_party/bounds_checking_function/include",
- ]
- deps = [
- "$hdf_uhdf_path/platform:libhdf_platform",
- "$hdf_uhdf_path/utils:libhdf_utils",
- "//base/hiviewdfx/hilog/interfaces/native/innerkits:libhilog",
- ]
- cflags = [
- "-Wall",
- "-Wextra",
- "-Werror",
- "-Wno-format",
- "-Wno-format-extra-args",
- ]
- part_name = "product_rk3568"
- install_enable = true
- }
编辑//vendor/lockzhiner/rk3568/samples/BUILD.gn,开启编译选项。具体如下:
- "b06_platform_device_i2c/app:rk3568_i2c_test",
建议使用docker编译方法,运行如下:
- hb set -root .
- hb set
- # 选择lockzhiner下的rk3568编译分支。
- hb build -f
运行如下:
- # rk3568_i2c_test -n 2 -a 115 -r 0 -l 1
- i2c number: 2
- i2c slave address: 115
- i2c reg address: 0
- i2c reg value: 0
- i2c read data length: 1
- i2c flags read: 1
- i2c flags addr 10bit: 0
- i2c flags read no ack: 0
- i2c flags ignore no ack: 0
- i2c flags no start: 0
- i2c flags stop: 0
- I2cTransfer success and read data length = 1
- rbuff[0] = 0x20
- #
在调试过程中,OpenHarmony还提供Linux i2c-tools工具。
(1)查看i2c控制器
- # i2cdetect -l
- i2c-1 i2c rk3x-i2c I2C Adapter
- i2c-6 i2c DesignWare HDMI I2C Adapter
- i2c-2 i2c rk3x-i2c I2C Adapter
- i2c-0 i2c rk3x-i2c I2C Adapter
- i2c-5 i2c rk3x-i2c I2C Adapter
- #
- # i2cdetect -y 2
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f
- 00: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 10: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 20: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 30: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 40: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 50: -- 51 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 60: -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- --
- 70: -- -- -- 73 -- -- -- --
- #
- # i2cdump -y 2 0x73
- 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 a b c d e f 0123456789abcdef
- 00: 20 76 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 v?.............
- 10: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
- 20: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
- 30: 00 00 29 01 00 01 00 09 15 0a 12 80 04 00 05 00 ..)?.?.??????.?.
- 40: 02 ff ff 00 00 00 60 20 20 03 c8 00 14 00 1a 14 ???...` ??.?.??
- 50: 00 05 00 00 14 20 03 02 20 00 00 02 02 00 00 3f .?..? ?? ..??..?
- 60: 23 23 00 03 f7 03 d9 03 01 c8 40 00 00 04 00 00 ##.???????@..?..
- 70: 80 00 00 00 f0 00 3f ff ff 7f 7f f2 34 92 00 00 ?...?.??????4?..
- 80: 66 66 0c 20 20 00 10 00 05 18 10 10 37 00 f0 81 ff? .?.????7.??
- 90: 0c 06 1e 0d 0a 0c 0a 04 0a 41 0a 0a 2b 33 ae f9 ?????????A??+3??
- a0: 48 13 10 08 30 11 10 08 24 04 1e 1e 00 00 00 00 H???0???$???....
- b0: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
- c0: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 1a 0d 03 63 ............???c
- d0: 22 0f 88 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 "??.............
- e0: 01 04 41 d6 00 0c 0a 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 07 00 ??A?.??.......?.
- f0: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ................
- #
回帖高级模式
声明:本文内容及配图由入驻作者撰写或者入驻合作网站授权转载。文章观点仅代表作者本人,不代表电子发烧友网立场。文章及其配图仅供工程师学习之用,如有内容图片侵权或者其他问题,请联系本站作侵删。 侵权投诉